Page 71 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 71
5 Neuroendocrinology 39
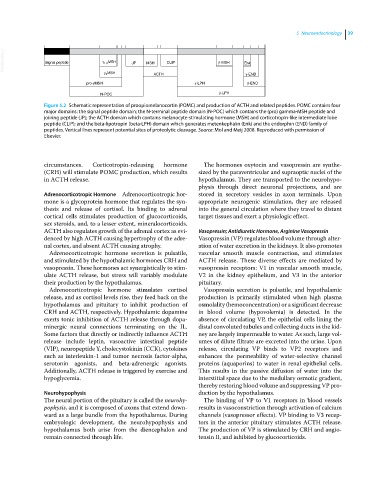
VetBooks.ir Signal peptide 1,2 MSH JP MSH CLIP -MSH Enk
3 MSH ACTH -END
pro- MSH -LPH -END
N-POC -LPH
Figure 5.2 Schematic representation of proopiomelanocortin (POMC) and production of ACTH and related peptides. POMC contains four
major domains: the signal peptide domain; the N‐terminal peptide domain (N‐POC) which contains the (pro) gamma‐MSH peptide and
joining peptide (JP); the ACTH domain which contains melanocyte‐stimulating hormone (MSH) and corticotropin‐like intermediate lobe
peptide (CLIP); and the beta‐lipotropin (beta‐LPH) domain which generates metenkephalin (Enk) and the endorphin (END) family of
peptides. Vertical lines represent potential sites of proteolytic cleavage. Source: Mol and Meij 2008. Reproduced with permission of
Elsevier.
circumstances. Corticotropin‐releasing hormone The hormones oxytocin and vasopressin are synthe-
(CRH) will stimulate POMC production, which results sized by the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the
in ACTH release. hypothalamus. They are transported to the neurohypo-
physis through direct neuronal projections, and are
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Adrenocorticotropic hor- stored in secretory vesicles in axon terminals. Upon
mone is a glycoprotein hormone that regulates the syn- appropriate neurogenic stimulation, they are released
thesis and release of cortisol. Its binding to adrenal into the general circulation where they travel to distant
cortical cells stimulates production of glucocorticoids, target tissues and exert a physiologic effect.
sex steroids, and, to a lesser extent, mineralocorticoids.
ACTH also regulates growth of the adrenal cortex as evi- Vasopressin; Antidiuretic Hormone, Arginine Vasopressin
denced by high ACTH causing hypertrophy of the adre- Vasopressin (VP) regulates blood volume through alter-
nal cortex, and absent ACTH causing atrophy. ation of water excretion in the kidneys. It also promotes
Adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion is pulsatile, vascular smooth muscle contraction, and stimulates
and stimulated by the hypothalamic hormones CRH and ACTH release. These diverse effects are mediated by
vasopressin. These hormones act synergistically to stim- vasopressin receptors: V1 in vascular smooth muscle,
ulate ACTH release, but stress will variably modulate V2 in the kidney epithelium, and V3 in the anterior
their production by the hypothalamus. pituitary.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulates cortisol Vasopressin secretion is pulsatile, and hypothalamic
release, and as cortisol levels rise, they feed back on the production is primarily stimulated when high plasma
hypothalamus and pituitary to inhibit production of osmolality (hemoconcentration) or a significant decrease
CRH and ACTH, respectively. Hypothalamic dopamine in blood volume (hypovolemia) is detected. In the
exerts tonic inhibition of ACTH release through dopa- absence of circulating VP, the epithelial cells lining the
minergic neural connections terminating on the IL. distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts in the kid-
Some factors that directly or indirectly influence ACTH ney are largely impermeable to water. As such, large vol-
release include leptin, vasoactive intestinal peptide umes of dilute filtrate are excreted into the urine. Upon
(VIP), neuropeptide Y, cholecystokinin (CCK), cytokines release, circulating VP binds to VP2 receptors and
such as interleukin‐1 and tumor necrosis factor‐alpha, enhances the permeability of water‐selective channel
serotonin agonists, and beta‐adrenergic agonists. proteins (aquaporins) to water in renal epithelial cells.
Additionally, ACTH release is triggered by exercise and This results in the passive diffusion of water into the
hypoglycemia. interstitial space due to the medullary osmotic gradient,
thereby restoring blood volume and suppressing VP pro-
Neurohypophysis duction by the hypothalamus.
The neural portion of the pituitary is called the neurohy- The binding of VP to V1 receptors in blood vessels
pophysis, and it is composed of axons that extend down- results in vasoconstriction through activation of calcium
ward as a large bundle from the hypothalamus. During channels (vasopressor effects). VP binding to V3 recep-
embryologic development, the neurohypophysis and tors in the anterior pituitary stimulates ACTH release.
hypothalamus both arise from the diencephalon and The production of VP is stimulated by CRH and angio-
remain connected through life. tensin II, and inhibited by glucocorticoids.