Page 69 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 69
5 Neuroendocrinology 37
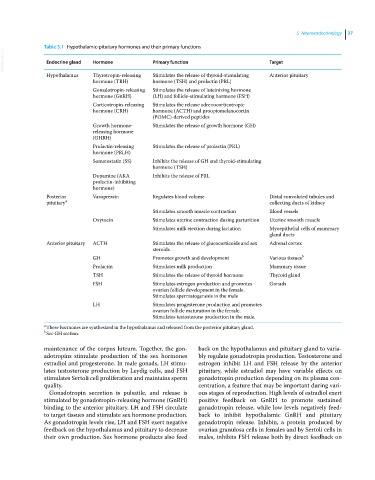
Table 5.1 Hypothalamic‐pituitary hormones and their primary functions
VetBooks.ir Endocrine gland Hormone Primary function Target
Hypothalamus Thyrotropin‐releasing Stimulates the release of thyroid‐stimulating Anterior pituitary
hormone (TRH) hormone (TSH) and prolactin (PRL)
Gonadotropin‐releasing Stimulates the release of luteinizing hormone
hormone (GnRH) (LH) and follicle‐stimulating hormone (FSH)
Corticotropin‐releasing Stimulates the release adrenocorticotropic
hormone (CRH) hormone (ACTH) and proopiomelanocortin
(POMC)‐derived peptides
Growth hormone‐ Stimulates the release of growth hormone (GH)
releasing hormone
(GHRH)
Prolactin‐releasing Stimulates the release of prolactin (PRL)
hormone (PRLH)
Somatostatin (SS) Inhibits the release of GH and thyroid‐stimulating
hormone (TSH)
Dopamine (AKA Inhibits the release of PRL
prolactin‐inhibiting
hormone)
Posterior Vasopressin Regulates blood volume Distal convoluted tubules and
pituitary a collecting ducts of kidney
Stimulates smooth muscle contraction Blood vessels
Oxytocin Stimulates uterine contraction during parturition Uterine smooth muscle
Stimulates milk ejection during lactation Myoepithelial cells of mammary
gland ducts
Anterior pituitary ACTH Stimulates the release of glucocorticoids and sex Adrenal cortex
steroids
GH Promotes growth and development Various tissues b
Prolactin Stimulates milk production Mammary tissue
TSH Stimulates the release of thyroid hormone Thyroid gland
FSH Stimulates estrogen production and promotes Gonads
ovarian follicle development in the female.
Stimulates spermatogenesis in the male
LH Stimulates progesterone production and promotes
ovarian follicle maturation in the female.
Stimulates testosterone production in the male.
a These hormones are synthesized in the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary gland.
b See GH section.
maintenance of the corpus luteum. Together, the gon- back on the hypothalamus and pituitary gland to varia-
adotropins stimulate production of the sex hormones bly regulate gonadotropin production. Testosterone and
estradiol and progesterone. In male gonads, LH stimu- estrogen inhibit LH and FSH release by the anterior
lates testosterone production by Leydig cells, and FSH pituitary, while estradiol may have variable effects on
stimulates Sertoli cell proliferation and maintains sperm gonadotropin production depending on its plasma con-
quality. centration, a feature that may be important during vari-
Gonadotropin secretion is pulsatile, and release is ous stages of reproduction. High levels of estradiol exert
stimulated by gonadotropin‐releasing hormone (GnRH) positive feedback on GnRH to promote sustained
binding to the anterior pituitary. LH and FSH circulate gonadotropin release, while low levels negatively feed-
to target tissues and stimulate sex hormone production. back to inhibit hypothalamic GnRH and pituitary
As gonadotropin levels rise, LH and FSH exert negative gonadotropin release. Inhibin, a protein produced by
feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary to decrease ovarian granulosa cells in females and by Sertoli cells in
their own production. Sex hormone products also feed males, inhibits FSH release both by direct feedback on