Page 408 - Canine Lameness
P. 408
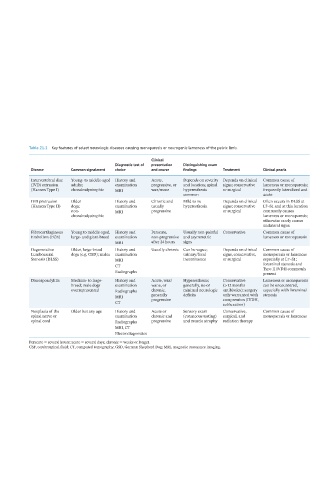
Table 21.1 Key features of select neurologic diseases causing monoparesis or neurogenic lameness of the pelvic limb.
Clinical
Diagnostic test of presentation Distinguishing exam
Disease Common signalment choice and course findings Treatment Clinical pearls
Intervertebral disc Young‐ to middle‐aged History and Acute, Depends on severity Depends on clinical Common cause of
(IVD) extrusion adults; examination progressive, or and location; spinal signs; conservative lameness or monoparesis;
(Hansen Type I) chondrodystrophic MRI wax/wane hyperesthesia or surgical frequently lateralized and
common acute
IVD protrusion Older History and Chronic and Mild to no Depends on clinical Often occurs in DLSS at
(Hansen Type II) dogs; examination usually hyperesthesia signs; conservative L7–S1 and at this location
non‐ MRI progressive or surgical commonly causes
chondrodystrophic lameness or monoparesis;
otherwise rarely causes
unilateral signs
Fibrocartilaginous Young to middle‐aged, History and Peracute, Usually non‐painful Conservative Common cause of
Embolism (FCE) large- and giant-breed examination non‐progressive and asymmetric lameness or monoparesis
MRI after 24 hours signs
Degenerative Older, large‐breed History and Usually chronic Can be vague; Depends on clinical Common cause of
Lumbosacral dogs (e.g. GSD); males examination urinary/fecal signs, conservative, monoparesis or lameness
Stenosis (DLSS) MRI incontinence or surgical especially at L7–S1;
CT foraminal stenosis and
Type II IVDH commonly
Radiographs present
Discospondylitis Medium- to large- History and Acute, wax/ Hyperesthesia; Conservative Lameness or monoparesis
breed; male dogs examination wane, or generally, no or (>12 months can be encountered,
overrepresented Radiographs chronic, minimal neurologic antibiotics); surgery especially with foraminal
MRI generally deficits only warranted with stenosis
progressive
compression (IVDH,
CT subluxation)
Neoplasia of the Older but any age History and Acute or Sensory exam Conservative, Common cause of
spinal nerve or examination chronic and (cutaneous testing) surgical, and monoparesis or lameness
spinal cord Radiographs progressive and muscle atrophy radiation therapy
MRI, CT
Electrodiagnostics
Peracute = several hours; acute = several days; chronic = weeks or longer.
CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; CT, computed tomography; GSD, German Shepherd Dog; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
0004507104.INDD 380 12/10/2019 1:51:45 PM