Page 167 - Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition
P. 167
Commercial Pet Foods 169
erences for mouth feel and the surface-to-volume ratio of cer-
VetBooks.ir tain shapes of dry kibbles.
Vision
Vision is important to the hunting and prey-seeking behav-
ior of wild animals. However, any relationship between the lim-
ited color vision of dogs and cats and their preference for a
food’s color is unknown.Thus, the degree to which visual stim-
uli influence food preference is speculative. Highly manipulat-
ed food colorings are common, but are probably more appeal-
ing to pet owners than to pets.
FACTORS AFFECTING FOOD
PREFERENCES
Water Content
Dog and cat food preferences and moisture content correlate
positively. On average, moist foods are preferred to semi-moist
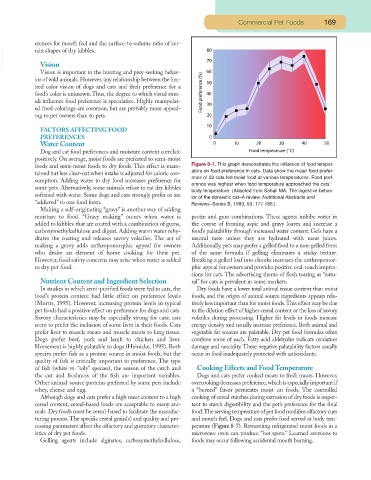
foods and semi-moist foods to dry foods. This effect is main- Figure 8-7. This graph demonstrates the influence of food temper-
ature on food preference in cats. Data show the mean food prefer-
tained but less clear-cut when intake is adjusted for caloric con-
ence of 23 cats fed moist food at various temperatures. Food pref-
sumption. Adding water to dry food increases preference for
erence was highest when food temperature approached the cats’
some pets. Alternatively, some animals refuse to eat dry kibbles
body temperature. (Adapted from Sohail MA. The ingestive behav-
softened with water. Some dogs and cats strongly prefer or are
ior of the domestic cat–A review. Nutritional Abstracts and
“addicted” to one food form. Reviews–Series B, 1983; 53: 177-186.)
Making a self-originating “gravy” is another way of adding
moisture to food. “Gravy making” occurs when water is pectin and gum combinations. These agents imbibe water in
added to kibbles that are coated with a combination of gums, the course of forming aspic and gravy loaves and increase a
carboxymethylcellulose and digest. Adding warm water rehy- food’s palatability through increased water content. Gels have a
drates the coating and releases savory volatiles. The act of neutral taste unless they are hydrated with meat juices.
making a gravy adds anthropomorphic appeal for owners Additionally, pets may prefer a gelled food to a non-gelled form
who desire an element of home cooking for their pet. of the same formula if gelling eliminates a sticky texture.
However, food safety concerns may arise when water is added Breaking a gelled loaf into chunks increases the anthropomor-
to dry pet food. phic appeal for owners and provides positive oral-touch impres-
sions for cats. The advertising theme of flesh tearing as “natu-
Nutrient Content and Ingredient Selection ral” for cats is prevalent in some markets.
In studies in which semi-purified foods were fed to cats, the Dry foods have a lower total animal tissue content than moist
food’s protein content had little effect on preference levels foods, and the origin of animal source ingredients appears rela-
(Morris, 1995). However, increasing protein levels in typical tively less important than for moist foods.This effect may be due
pet foods had a positive effect on preference for dogs and cats. to the dilution effect of higher cereal content or the loss of savory
Savory characteristics may be especially strong for cats; cats volatiles during processing. Higher fat levels in foods increase
seem to prefer the inclusion of some liver in their foods. Cats energy density and usually increase preference. Both animal and
prefer liver to muscle meats and muscle meats to lung tissue. vegetable fat sources are palatable. Dry pet food formulas often
Dogs prefer beef, pork and lamb to chicken and liver. combine some of each. Fatty acid aldehydes indicate oxidation
Horsemeat is highly palatable to dogs (Heinicke, 1995). Both damage and rancidity. These negative palatability factors usually
species prefer fish as a protein source in moist foods, but the occur in food inadequately protected with antioxidants.
quality of fish is critically important to preference. The type
of fish (white vs. “oily” species), the season of the catch and Cooking Effects and Food Temperature
the cut and freshness of the fish are important variables. Dogs and cats prefer cooked meats to fresh meats. However,
Other animal-source proteins preferred by some pets include overcooking decreases preference,which is especially important if
whey, cheese and egg. a “burned” flavor permeates moist cat foods. The controlled
Although dogs and cats prefer a high meat content to a high cooking of cereal starches during extrusion of dry foods is impor-
cereal content, cereal-based foods are acceptable to many ani- tant to starch digestibility and the pet’s preference for the final
mals. Dry foods must be cereal-based to facilitate the manufac- food.The serving temperature of pet food modifies olfactory cues
turing process.The specific cereal grain(s) and quality and pro- and mouth feel. Dogs and cats prefer food served at body tem-
cessing parameters affect the olfactory and gustatory character- perature (Figure 8-7). Rewarming refrigerated moist foods in a
istics of dry pet foods. microwave oven can produce “hot spots.” Learned aversions to
Gelling agents include alginates, carboxymethylcellulose, foods may occur following accidental mouth burning.