Page 1044 - Saunders Comprehensive Review For NCLEX-RN
P. 1044
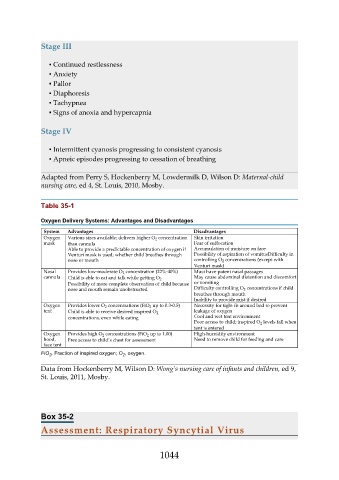
Stage III
▪ Continued restlessness
▪ Anxiety
▪ Pallor
▪ Diaphoresis
▪ Tachypnea
▪ Signs of anoxia and hypercapnia
Stage IV
▪ Intermittent cyanosis progressing to consistent cyanosis
▪ Apneic episodes progressing to cessation of breathing
Adapted from Perry S, Hockenberry M, Lowdermilk D, Wilson D: Maternal-child
nursing care, ed 4, St. Louis, 2010, Mosby.
Table 35-1
Oxygen Delivery Systems: Advantages and Disadvantages
System Advantages Disadvantages
Oxygen Various sizes available; delivers higher O 2 concentration Skin irritation
mask than cannula Fear of suffocation
Able to provide a predictable concentration of oxygen if Accumulation of moisture on face
Venturi mask is used, whether child breathes through Possibility of aspiration of vomitusDifficulty in
nose or mouth controlling O 2 concentrations (except with
Venturi mask)
Nasal Provides low-moderate O 2 concentration (22%-40%) Must have patent nasal passages
cannula May cause abdominal distention and discomfort
Child is able to eat and talk while getting O 2
Possibility of more complete observation of child because or vomiting
nose and mouth remain unobstructed Difficulty controlling O 2 concentrations if child
breathes through mouth
Inability to provide mist if desired
Oxygen Provides lower O 2 concentrations (FiO 2 up to 0.3-0.5) Necessity for tight fit around bed to prevent
tent Child is able to receive desired inspired O 2 leakage of oxygen
concentrations, even while eating Cool and wet tent environment
Poor access to child; inspired O 2 levels fall when
tent is entered
Oxygen Provides high O 2 concentrations (FiO 2 up to 1.00) High-humidity environment
hood, Free access to child’s chest for assessment Need to remove child for feeding and care
face tent
FiO , Fraction of inspired oxygen; O , oxygen.
2
2
Data from Hockenberry M, Wilson D: Wong’s nursing care of infants and children, ed 9,
St. Louis, 2011, Mosby.
Box 35-2
Assessment: Respiratory Syncytial Virus
1044