Page 55 - Math SL HB Sem 3
P. 55
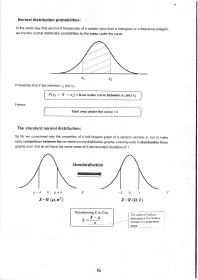
Normal distribution probabilities:
ln the same way that we found frequencies of a certain class from a histogram or a frequency polygon,
we find the normal distribution probabilities by the areas under the curve.
xl xz
Probability that X lies between x, and r, ,
P(xy < X l xz)= Area under curve between xlandx2
Hence,
Total area under the curve = 1
The standard normal distribution:
so far we considered only the properties of a bell-shaped graph of a random variable x, but to make
easy comParison between two or more normal distribution graphs, one may wish to standardise those
graphs such that all will have the same mean of0 and standard deviation of .1.
Stondardisotion
-D,
p- o 0 11+ o x -1 0 1 Z
-./
X-N (1t,oz) z-N (o,r)
Transforming XloZby
x-1t The uelue ofZtells us
Z how many o the random
o wiable X is awaY Aom
meaD.
IL