Page 56 - Math SL HB Sem 3
P. 56
,\ Example:
For X-IV (20 ,32) and X = 15, the conesponding Z-value
z =" ,'o = - t,a? gon"", ,o, ,ig.1is:1
r)
& Not",
standardisation only transforms the value of x to another value but caluses no change to the area
under the curve and thus the probabilities. Thus, P(X = 75) = P(z = 1'67)'
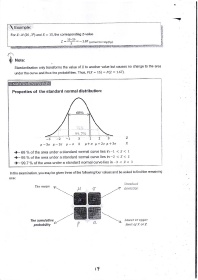
Properties of the standard normal distribution:
684/o
-3 -2 -l 0 123 Z
|-3o p-\o P-o O lt+o tt+zo P+3o X
,- 68 % of the area under a standard normal curve lies in -1 < z < I
t- 95 % of the area under a standard normal curye lies in -z < z < z
.,- 99.7 % of the area under a standard normal curve lies in -3 < z < 3 I
ln the examination, you may be given three of the following four values and be asked to find the remaining
one:
StandErd
Ihe meon 5- tt d- 4 devictia*
-EE
t=
t:'re Lower or up9er
The cumulotive
probability limit af X or Z
t7