Page 166 - Clinical Pearls in Cardiology
P. 166
154 Clinical Pearls in Cardiology
chest discomfort may present with ST segment elevation
(STEMI) or without ST segment elevation in the ECG.
Patients without ST segment elevation in the ECG
may have either unstable angina or non-ST segment
elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI). In patients
with unstable angina or NSTEMI, the electrocardiogram
may show ST/T wave changes including ST depression
and T wave inversion. The distinction between unstable
angina and NSTEMI is ultimately made on the basis of
the presence or absence of elevated levels of cardiac
biomarkers in the blood (elevated levels of either CK–MB
or cardiac specific troponins like troponin T or troponin
I indicate the occurrence of acute myocardial infarction).
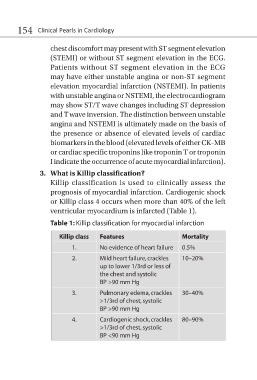
3. What is Killip classification?
Killip classification is used to clinically assess the
prognosis of myocardial infarction. Cardiogenic shock
or Killip class 4 occurs when more than 40% of the left
ventricular myocardium is infarcted (Table 1).
Table 1: Killip classification for myocardial infarction
Killip class Features Mortality
1. No evidence of heart failure 0.5%
2. Mild heart failure, crackles 10–20%
up to lower 1/3rd or less of
the chest and systolic
BP >90 mm Hg
3. Pulmonary edema, crackles 30–40%
>1/3rd of chest, systolic
BP >90 mm Hg
4. Cardiogenic shock, crackles 80–90%
>1/3rd of chest, systolic
BP <90 mm Hg