Page 48 - Children Bookt.pdf
P. 48
&
@
'
^£
+/Z]
:+#&`
]
6
&
'
'
'
]
&
+/6
#
$
¤
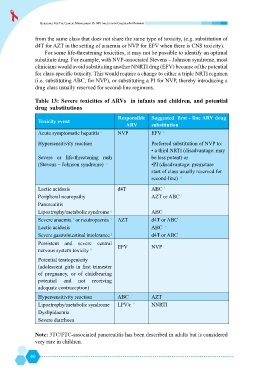
clinicians would avoid substituting another NNRTI drug (EFV) because of the potential
6
&
;
+!
(i.e. substituting ABC, for NVP), or substituting a PI for NVP, thereby introducing a
drug class usually reserved for second-line regimens.
@Uj[ &> x
drug substitutions
Responsible ## &>#
@ "
ARV substitution
b
Acute symptomatic hepatitis a NVP EFV
Hypersensitivity reaction /
'+/*
+!@$
*
Severe or life-threatening rash be less potent) or
(Stevens – Johnson syndrome) c /!@$
*
start of class usually reserved for
second-line)
d
Lactic acidosis d4T ABC e
Peripheral neuropathy AZT or ABC f
Pancreatitis
Lipoatrophy/metabolic syndrome g ABC
h
Severe anaemia or neutropaenia i AZT d4T or ABC
Lactic acidosis ABC e
Severe gastrointestinal intolerance 8 d4T or ABC
Persistent and severe central
EFV NVP
k
$
&
Potential teratogenicity
@
of pregnancy, or of childbearing
potential and not receiving
adequate contraception)
Hypersensitivity reaction ABC AZT
Lipoatrophy/metabolic syndrome LPV/r l NNRTI
Dyslipidaemia
Severe diarrhoea
Note: 3TC/FTC-associated pancreatitis has been described in adults but is considered
very rare in children.
40