Page 66 - Children Bookt.pdf
P. 66
6.
6
&
'
9
'
!6
&
6
breast milk as an interim feeding strategy*
- in special circumstances such as when the infant is born with low birth weight
or is otherwise ill in the neonatal period and unable to breastfeed; or
- when the mother is unwell and temporarily unable to breastfeed or has a
temporary breast health problem such as mastitis; or
- to assist mothers to stop breastfeeding; or
- if antiretroviral drugs are temporarily not available.
7. When the infant is HIV-infected
If infants and young children are known to be HIV-infected, mothers are
&$
'
&
life and continue breastfeeding as per the recom mendations for the general
population, that is, up to two years or beyond.
Strategies to reduce breast milk transmission
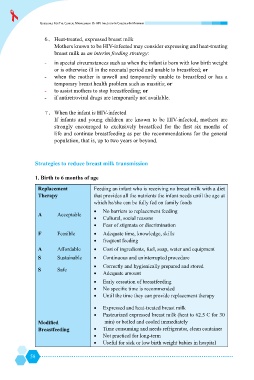
1. Birth to 6 months of age
Replacement Feeding an infant who is receiving no breast milk with a diet
Therapy that provides all the nutrients the infant needs until the age at
which he/she can be fully fed on family foods
No barriers to replacement feeding
A Acceptable
Cultural, social reasons
Fear of stigmata or discrimination
F Feasible Adequate time, knowledge, skills
frequent feeding
A Affordable Cost of ingredients, fuel, soap, water and equipment
S Sustainable Continuous and uninterrupted procedure
Correctly and hygienically prepared and stored
S Safe
Adequate amount
Early cessation of breastfeeding
+
Until the time they can provide replacement therapy
Z&
6
'
/
~
&
'
@
_{:x
^ min) or boiled and cooled immediately
Breastfeeding Time consuming and needs refrigerator, clean container
Not practical for long-term
Useful for sick or low birth weight babies in hospital
58