Page 16 - TVH 2000 Anniversary Shipwreck Project
P. 16
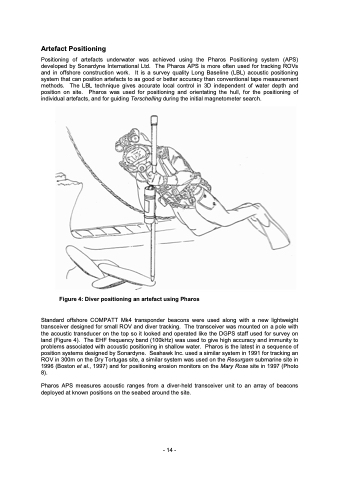
Artefact Positioning Positioning of artefacts underwater was achieved using the Pharos Positioning system (APS) developed by Sonardyne International Ltd. The Pharos APS is more often used for tracking ROVs and in offshore construction work. It is a survey quality Long Baseline (LBL) acoustic positioning system that can position artefacts to as good or better accuracy than conventional tape measurement methods. The LBL technique gives accurate local control in 3D independent of water depth and position on site. Pharos was used for positioning and orientating the hull, for the positioning of individual artefacts, and for guiding Terschelling during the initial magnetometer search. Figure 4: Diver positioning an artefact using Pharos Standard offshore COMPATT Mk4 transponder beacons were used along with a new lightweight transceiver designed for small ROV and diver tracking. The transceiver was mounted on a pole with the acoustic transducer on the top so it looked and operated like the DGPS staff used for survey on land (Figure 4). The EHF frequency band (100kHz) was used to give high accuracy and immunity to problems associated with acoustic positioning in shallow water. Pharos is the latest in a sequence of position systems designed by Sonardyne. Seahawk Inc. used a similar system in 1991 for tracking an ROV in 300m on the Dry Tortugas site, a similar system was used on the Resurgam submarine site in 1996 (Boston et al., 1997) and for positioning erosion monitors on the Mary Rose site in 1997 (Photo 8). Pharos APS measures acoustic ranges from a diver-held transceiver unit to an array of beacons deployed at known positions on the seabed around the site. - 14 -