Page 298 - Data Science Algorithms in a Week
P. 298
Artificial Intelligence for the Modeling and Prediction ... 279
published by Krogh (2008), Dohnal et al. (2005), and Zupan & Gasteiger (1991). These
are listed in order of increasing complexity for a smooth progression.
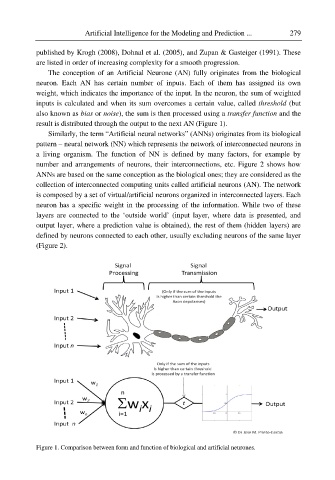
The conception of an Artificial Neurone (AN) fully originates from the biological
neuron. Each AN has certain number of inputs. Each of them has assigned its own
weight, which indicates the importance of the input. In the neuron, the sum of weighted
inputs is calculated and when its sum overcomes a certain value, called threshold (but
also known as bias or noise), the sum is then processed using a transfer function and the
result is distributed through the output to the next AN (Figure 1).
Similarly, the term “Artificial neural networks” (ANNs) originates from its biological
pattern – neural network (NN) which represents the network of interconnected neurons in
a living organism. The function of NN is defined by many factors, for example by
number and arrangements of neurons, their interconnections, etc. Figure 2 shows how
ANNs are based on the same conception as the biological ones; they are considered as the
collection of interconnected computing units called artificial neurons (AN). The network
is composed by a set of virtual/artificial neurons organized in interconnected layers. Each
neuron has a specific weight in the processing of the information. While two of these
layers are connected to the ‘outside world’ (input layer, where data is presented, and
output layer, where a prediction value is obtained), the rest of them (hidden layers) are
defined by neurons connected to each other, usually excluding neurons of the same layer
(Figure 2).
Figure 1. Comparison between form and function of biological and artificial neurones.