Page 300 - Data Science Algorithms in a Week
P. 300
Artificial Intelligence for the Modeling and Prediction ... 281
©Jose M Prieto
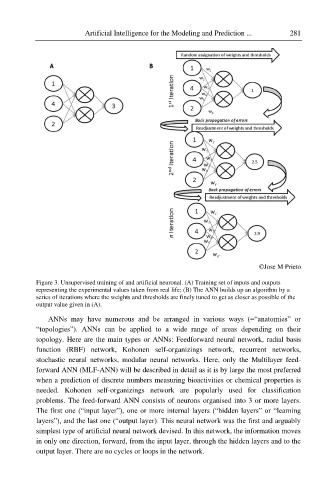
Figure 3. Unsupervised training of and artificial neuronal. (A) Training set of inputs and outputs
representing the experimental values taken from real life; (B) The ANN builds up an algorithm by a
series of iterations where the weights and thresholds are finely tuned to get as closer as possible of the
output value given in (A).
ANNs may have numerous and be arranged in various ways (=“anatomies” or
“topologies”). ANNs can be applied to a wide range of areas depending on their
topology. Here are the main types or ANNs: Feedforward neural network, radial basis
function (RBF) network, Kohonen self-organizings network, recurrent networks,
stochastic neural networks, modular neural networks. Here, only the Multilayer feed-
forward ANN (MLF-ANN) will be described in detail as it is by large the most preferred
when a prediction of discrete numbers measuring bioactivities or chemical properties is
needed. Kohonen self-organizings network are popularly used for classification
problems. The feed-forward ANN consists of neurons organised into 3 or more layers.
The first one (“input layer”), one or more internal layers (“hidden layers” or “learning
layers”), and the last one (“output layer). This neural network was the first and arguably
simplest type of artificial neural network devised. In this network, the information moves
in only one direction, forward, from the input layer, through the hidden layers and to the
output layer. There are no cycles or loops in the network.