Page 33 - The Insurance Times February 2025
P. 33
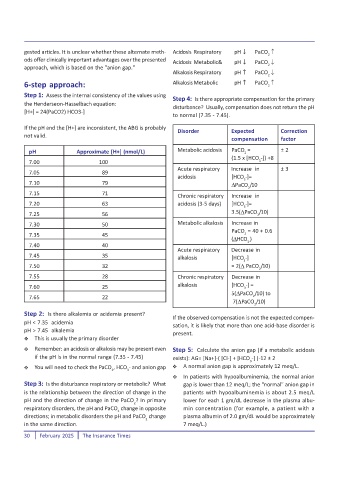
gested articles. It is unclear whether these alternate meth- Acidosis Respiratory pH PaCO
2
ods offer clinically important advantages over the presented Acidosis Metabolic& pH PaCO
approach, which is based on the "anion gap." 2
AlkalosisRespiratory pH PaCO
2
6-step approach: AlkalosisMetabolic pH PaCO
2
Step 1: Assess the internal consistency of the values using
Step 4: Is there appropriate compensation for the primary
the Henderseon-Hasselbach equation:
disturbance? Usually, compensation does not return the pH
[H+] = 24(PaCO2) HCO3-]
to normal (7.35 - 7.45).
If the pH and the [H+] are inconsistent, the ABG is probably
Disorder Expected Correction
not valid.
compensation factor
pH Approximate [H+] (nmol/L) Metabolic acidosis PaCO = ± 2
2
(1.5 x [HCO -]) +8
7.00 100 3
Acute respiratory Increase in ± 3
7.05 89
acidosis [HCO -]=
3
7.10 79 PaCO /10
2
7.15 71
Chronic respiratory Increase in
7.20 63 acidosis (3-5 days) [HCO -]=
3
7.25 56 3.5( PaCO /10)
2
7.30 50 Metabolic alkalosis Increase in
PaCO = 40 + 0.6
7.35 45 2
( HCO )
3-
7.40 40
Acute respiratory Decrease in
7.45 35 alkalosis [HCO -]
3
7.50 32 = 2( PaCO /10)
2
7.55 28 Chronic respiratory Decrease in
7.60 25 alkalosis [HCO -] =
3
5( PaCO /10) to
7.65 22 2
7( PaCO /10)
2
Step 2: Is there alkalemia or acidemia present?
If the observed compensation is not the expected compen-
pH < 7.35 acidemia
sation, it is likely that more than one acid-base disorder is
pH > 7.45 alkalemia
present.
This is usually the primary disorder
Remember: an acidosis or alkalosis may be present even Step 5: Calculate the anion gap (if a metabolic acidosis
if the pH is in the normal range (7.35 - 7.45) exists): AG= [Na+]-( [Cl-] + [HCO -] )-12 ± 2
3
You will need to check the PaCO , HCO - and anion gap A normal anion gap is approximately 12 meq/L.
2 3
In patients with hypoalbuminemia, the normal anion
Step 3: Is the disturbance respiratory or metabolic? What gap is lower than 12 meq/L; the "normal" anion gap in
is the relationship between the direction of change in the patients with hypoalbuminemia is about 2.5 meq/L
pH and the direction of change in the PaCO ? In primary lower for each 1 gm/dL decrease in the plasma albu-
2
respiratory disorders, the pH and PaCO change in opposite min concentration (for example, a patient with a
2
directions; in metabolic disorders the pH and PaCO change plasma albumin of 2.0 gm/dL would be approximately
2
in the same direction. 7 meq/L.)
30 February 2025 The Insurance Times