Page 35 - The Insurance Times February 2025
P. 35
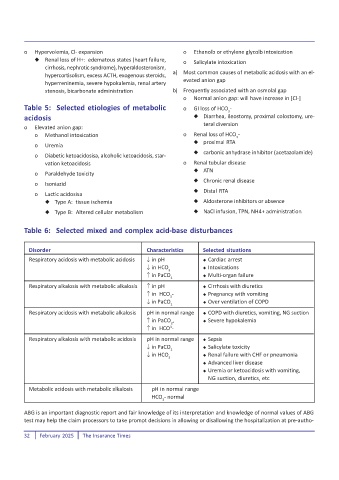
o Hypervolemia, Cl- expansion o Ethanolb or ethylene glycolb intoxication
Renal loss of H+: edematous states (heart failure, o Salicylate intoxication
cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome), hyperaldosteronism,
a) Most common causes of metabolic acidosis with an el-
hypercortisolism, excess ACTH, exogenous steroids,
evated anion gap
hyperreninemia, severe hypokalemia, renal artery
stenosis, bicarbonate administration b) Frequently associated with an osmolal gap
o Normal anion gap: will have increase in [Cl-]
Table 5: Selected etiologies of metabolic o GI loss of HCO -
3
acidosis Diarrhea, ileostomy, proximal colostomy, ure-
teral diversion
o Elevated anion gap:
o Methanol intoxication o Renal loss of HCO -
3
proximal RTA
o Uremia
carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (acetazolamide)
o Diabetic ketoacidosisa, alcoholic ketoacidosis, star-
vation ketoacidosis o Renal tubular disease
ATN
o Paraldehyde toxicity
Chronic renal disease
o Isoniazid
Distal RTA
o Lactic acidosisa
Type A: tissue ischemia Aldosterone inhibitors or absence
Type B: Altered cellular metabolism NaCl infusion, TPN, NH4+ administration
Table 6: Selected mixed and complex acid-base disturbances
Disorder Characteristics Selected situations
Respiratory acidosis with metabolic acidosis in pH Cardiac arrest
in HCO Intoxications
3
in PaCO Multi-organ failure
2
Respiratory alkalosis with metabolic alkalosis in pH Cirrhosis with diuretics
in HCO - Pregnancy with vomiting
3
in PaCO Over ventilation of COPD
2
Respiratory acidosis with metabolic alkalosis pH in normal range COPD with diuretics, vomiting, NG suction
in PaCO , Severe hypokalemia
2
in HCO -
3
Respiratory alkalosis with metabolic acidosis pH in normal range Sepsis
in PaCO Salicylate toxicity
2
in HCO Renal failure with CHF or pneumonia
3
Advanced liver disease
Uremia or ketoacidosis with vomiting,
NG suction, diuretics, etc
Metabolic acidosis with metabolic alkalosis pH in normal range
HCO - normal
3
ABG is an important diagnostic report and fair knowledge of its interpretation and knowledge of normal values of ABG
test may help the claim processors to take prompt decisions in allowing or disallowing the hospitalization at pre-autho-
32 February 2025 The Insurance Times