Page 19 - Essential Haematology
P. 19
Chapter 1 Haemopoiesis / 5
growth factors, adhesion molecules and cytokines tions maintain stem cell viability and production in
which support stem cells, e.g. the protein jagged, the stroma including stem cell factor (SCF) and
on stromal cells binds to a receptor NOTCH1 on jagged proteins expressed on stroma and their
stem cells which then becomes a transcription factor respective receptors KIT and NOTCH expressed
involved in the cell cycle. on stem cell.
Stem cells are able to traffic around the body
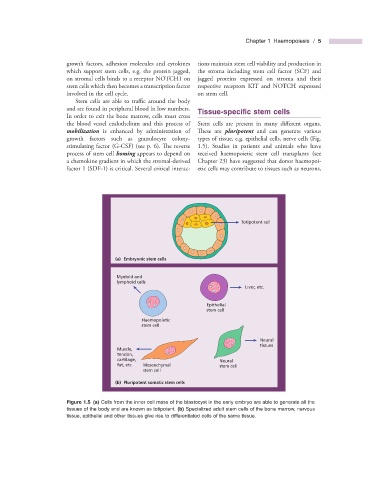
and are found in peripheral blood in low numbers. Tissue - s pecifi c s tem c ells
In order to exit the bone marrow, cells must cross
the blood vessel endothelium and this process of Stem cells are present in many diff erent organs.
mobilization is enhanced by administration of Th ese are pluripotent and can generate various
growth factors such as granulocyte colony - types of tissue, e.g. epithelial cells, nerve cells (Fig.
stimulating factor (G - CSF) (see p. 6 ). Th e reverse 1.5 ). Studies in patients and animals who have
process of stem cell homing appears to depend on received haemopoietic stem cell transplants (see
a chemokine gradient in which the stromal - derived Chapter 23 ) have suggested that donor haemopoi-
factor 1 (SDF - 1) is critical. Several critical interac- etic cells may contribute to tissues such as neurons,
Totipotent cell
(a) Embryonic stem cells
Myeloid and
lymphoid cells
Liver, etc.
Epithelial
stem cell
Haemopoietic
stem cell
Neural
tissues
Muscle,
tendon,
cartilage, Neural
fat, etc. Mesenchymal stem cell
stem cell
(b) Pluripotent somatic stem cells
Figure 1.5 (a) Cells from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst in the early embryo are able to generate all the
tissues of the body and are known as totipotent. (b) Specialized adult stem cells of the bone marrow, nervous
tissue, epithelial and other tissues give rise to differentiated cells of the same tissue.