Page 216 - Essential Haematology
P. 216
Receptor
Cell P P P P
membrane
(i) (ii) (iii)
P
JAK2 Activated JAK2 Growth factor
(a)
T
A T G T T T C T G A T G T G T C T G
PI3K Ras
Granulocytes
P P
A T G T G T C T G A T G T G T C T G
P Akt ERK/MAPK
T cells
STAT
(b)
Transcription
factors
Cell survival
Cell proliferation
(c)
Normal cell
Heterozygous JAK2 mutation (V617F)
Homozygous JAK2 mutation (V617F)
(d)
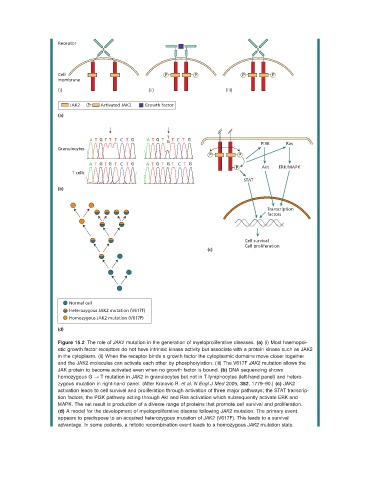
Figure 15.2 The role of JAK2 mutation in the generation of myeloproliferative diseases. (a) (i) Most haemopoi-
etic growth factor receptors do not have intrinsic kinase activity but associate with a protein kinase such as JAK2
in the cytoplasm. (ii) When the receptor binds a growth factor the cytoplasmic domains move closer together
and the JAK2 molecules can activate each other by phosphorylation. (iii) The V617F JAK2 mutation allows the
JAK protein to become activated even when no growth factor is bound. (b) DNA sequencing shows
homozygous G → T mutation in JAK2 in granulocytes but not in T lymphocytes (left - hand panel) and hetero-
zygous mutation in right - hand panel. (After Kralovic R. et al . N Engl J Med 2005, 352 , 1779 – 90.) (c) JAK2
activation leads to cell survival and proliferation through activation of three major pathways; the STAT transcrip-
tion factors, the PI3K pathway acting through Akt and Ras activation which subsequently activate ERK and
MAPK. The net result is production of a diverse range of proteins that promote cell survival and proliferation.
(d) A model for the development of myeloproliferative disease following JAK2 mutation. The primary event
appears to predispose to an acquired heterozygous mutation of JAK2 (V617F). This leads to a survival
advantage. In some patients, a mitotic recombination event leads to a homozygous JAK2 mutation state.