Page 218 - Essential Haematology
P. 218
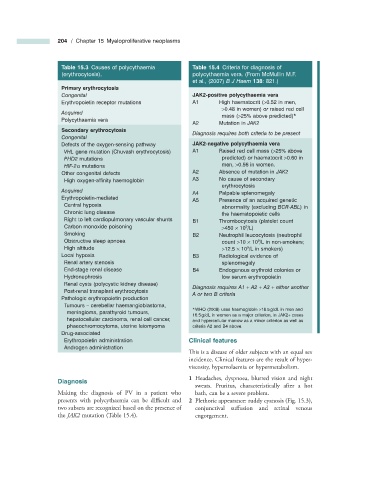
204 / Chapter 15 Myeloproliferative neoplasms
Table 15.3 Causes of polycythaemia Table 15.4 Criteria for diagnosis of
(erythrocytosis). polycythaemia vera. (From McMullin M.F.
et al., (2007) B J Haem 138 : 821.)
Primary erythrocytosis
Congenital JAK2 - positive polycythaemia vera
Erythropoietin receptor mutations A1 High haematocrit ( > 0.52 in men,
> 0.48 in women) or raised red cell
Acquired
mass ( > 25% above predicted) *
Polycythaemia vera
A2 Mutation in JAK2
Secondary erythrocytosis
Diagnosis requires both criteria to be present
Congenital
Defects of the oxygen - sensing pathway JAK2 - negative polycythaemia vera
VHL gene mutation (Chuvash erythrocytosis) A1 Raised red cell mass ( > 25% above
PHD2 mutations predicted) or haematocrit > 0.60 in
HIF - 2 α mutations men, > 0.56 in women.
Other congenital defects A2 Absence of mutation in JAK2
High oxygen - affi nity haemoglobin A3 No cause of secondary
erythrocytosis
Acquired A4 Palpable splenomegaly
Erythropoietin - mediated
A5 Presence of an acquired genetic
Central hypoxia
abnormality (excluding BCR - ABL ) in
Chronic lung disease the haematopoietic cells
Right to left cardiopulmonary vascular shunts B1 Thrombocytosis (platelet count
Carbon monoxide poisoning > 450 × 10 /L)
9
Smoking B2 Neutrophil leucocytosis (neutrophil
Obstructive sleep apnoea count > 10 × 10 /L in non - smokers;
9
9
High altitude > 12.5 × 10 /L in smokers)
Local hypoxia B3 Radiological evidence of
Renal artery stenosis splenomegaly
End - stage renal disease B4 Endogenous erythroid colonies or
Hydronephrosis low serum erythropoietin
Renal cysts (polycystic kidney disease)
Diagnosis requires A1 + A2 + A3 + either another
Post - renal transplant erythrocytosis
A or two B criteria
Pathologic erythropoietin production
Tumours – cerebellar haemangioblastoma,
* WHO (2008) uses haemoglobin > 18.5 g/dL in men and
meningioma, parathyroid tumours,
16.5 g/dL in women as a major criterion, in JAK2 + cases
hepatocellular carcinoma, renal cell cancer, and hypercellular marrow as a minor criterion as well as
phaeochromocytoma, uterine leiomyoma criteria A2 and B4 above.
Drug - associated
Erythropoietin administration Clinical f eatures
Androgen administration
This is a disease of older subjects with an equal sex
incidence. Clinical features are the result of hyper-
viscosity, hypervolaemia or hypermetabolism.
1 Headaches, dyspnoea, blurred vision and night
Diagnosis
sweats. Pruritus, characteristically after a hot
Making the diagnosis of PV in a patient who bath, can be a severe problem.
presents with polycythaemia can be diffi cult and 2 Plethoric appearance: ruddy cyanosis (Fig. 15.3 ),
two subsets are recognized based on the presence of conjunctival suffusion and retinal venous
the JAK2 mutation (Table 15.4 ). engorgement.