Page 1025 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1025
CHAPTER 56 Introduction to Toxicology: Occupational & Environmental 1011
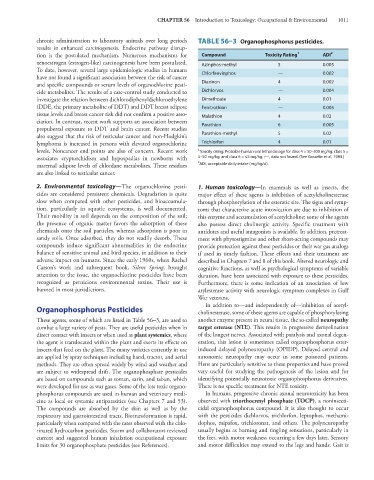
chronic administration to laboratory animals over long periods TABLE 56–3 Organophosphorus pesticides.
results in enhanced carcinogenesis. Endocrine pathway disrup-
tion is the postulated mechanism. Numerous mechanisms for Compound Toxicity Rating 1 ADI 2
xenoestrogen (estrogen-like) carcinogenesis have been postulated. Azinphos-methyl 5 0.005
To date, however, several large epidemiologic studies in humans Chlorfenvinphos — 0.002
have not found a significant association between the risk of cancer
and specific compounds or serum levels of organochlorine pesti- Diazinon 4 0.002
cide metabolites. The results of a case-control study conducted to Dichlorvos — 0.004
investigate the relation between dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene Dimethoate 4 0.01
(DDE, the primary metabolite of DDT) and DDT breast adipose Fenitrothion — 0.005
tissue levels and breast cancer risk did not confirm a positive asso- Malathion 4 0.02
ciation. In contrast, recent work supports an association between Parathion 6 0.005
prepubertal exposure to DDT and brain cancer. Recent studies
also suggest that the risk of testicular cancer and non-Hodgkin’s Parathion-methyl 5 0.02
lymphoma is increased in persons with elevated organochlorine Trichlorfon 4 0.01
levels. Noncancer end points are also of concern. Recent work 1 Toxicity rating: Probable human oral lethal dosage for class 4 = 50–500 mg/kg, class 5 =
associates cryptorchidism and hypospadias in newborns with 5–50 mg/kg, and class 6 = ≤5 mg/kg, ;—, data not found. (See Gosselin et al, 1984.)
maternal adipose levels of chlordane metabolites. These residues 2 ADI, acceptable daily intake (mg/kg/d).
are also linked to testicular cancer.
2. Environmental toxicology—The organochlorine pesti- 1. Human toxicology—In mammals as well as insects, the
cides are considered persistent chemicals. Degradation is quite major effect of these agents is inhibition of acetylcholinesterase
slow when compared with other pesticides, and bioaccumula- through phosphorylation of the esteratic site. The signs and symp-
tion, particularly in aquatic ecosystems, is well documented. toms that characterize acute intoxication are due to inhibition of
Their mobility in soil depends on the composition of the soil; this enzyme and accumulation of acetylcholine; some of the agents
the presence of organic matter favors the adsorption of these also possess direct cholinergic activity. Specific treatment with
chemicals onto the soil particles, whereas adsorption is poor in antidotes and useful antagonists is available. In addition, pretreat-
sandy soils. Once adsorbed, they do not readily desorb. These ment with physostigmine and other short-acting compounds may
compounds induce significant abnormalities in the endocrine provide protection against these pesticides or their war gas analogs
balance of sensitive animal and bird species, in addition to their if used in timely fashion. These effects and their treatment are
adverse impact on humans. Since the early 1960s, when Rachel described in Chapters 7 and 8 of this book. Altered neurologic and
Carson’s work and subsequent book, Silent Spring, brought cognitive functions, as well as psychological symptoms of variable
attention to the issue, the organochlorine pesticides have been duration, have been associated with exposure to these pesticides.
recognized as pernicious environmental toxins. Their use is Furthermore, there is some indication of an association of low
banned in most jurisdictions. arylesterase activity with neurologic symptom complexes in Gulf
War veterans.
In addition to—and independently of—inhibition of acetyl-
Organophosphorus Pesticides cholinesterase, some of these agents are capable of phosphorylating
These agents, some of which are listed in Table 56–3, are used to another enzyme present in neural tissue, the so-called neuropathy
combat a large variety of pests. They are useful pesticides when in target esterase (NTE). This results in progressive demyelination
direct contact with insects or when used as plant systemics, where of the longest nerves. Associated with paralysis and axonal degen-
the agent is translocated within the plant and exerts its effects on eration, this lesion is sometimes called organophosphorus ester-
insects that feed on the plant. The many varieties currently in use induced delayed polyneuropathy (OPIDP). Delayed central and
are applied by spray techniques including hand, tractor, and aerial autonomic neuropathy may occur in some poisoned patients.
methods. They are often spread widely by wind and weather and Hens are particularly sensitive to these properties and have proved
are subject to widespread drift. The organophosphate pesticides very useful for studying the pathogenesis of the lesion and for
are based on compounds such as soman, sarin, and tabun, which identifying potentially neurotoxic organophosphorus derivatives.
were developed for use as war gases. Some of the less toxic organo- There is no specific treatment for NTE toxicity.
phosphorus compounds are used in human and veterinary medi- In humans, progressive chronic axonal neurotoxicity has been
cine as local or systemic antiparasitics (see Chapters 7 and 53). observed with triorthocresyl phosphate (TOCP), a noninsecti-
The compounds are absorbed by the skin as well as by the cidal organophosphorus compound. It is also thought to occur
respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Biotransformation is rapid, with the pesticides dichlorvos, trichlorfon, leptophos, methami-
particularly when compared with the rates observed with the chlo- dophos, mipafox, trichloronat, and others. The polyneuropathy
rinated hydrocarbon pesticides. Storm and collaborators reviewed usually begins as burning and tingling sensations, particularly in
current and suggested human inhalation occupational exposure the feet, with motor weakness occurring a few days later. Sensory
limits for 30 organophosphate pesticides (see References). and motor difficulties may extend to the legs and hands. Gait is