Page 1026 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1026
1012 SECTION IX Toxicology
affected, and ataxia may be present. Central nervous system and for the organophosphorus pesticides. However, as described in
autonomic changes may develop still later. There is no specific Chapters 7 and 8, the binding is relatively weak, dissociation
treatment for this form of delayed neurotoxicity. The long-term occurs after minutes to hours, and clinical effects are of shorter
prognosis of NTE inhibition is highly variable. Reports of this duration than those observed with organophosphorus com-
type of neuropathy (and other toxicities) in pesticide manufactur- pounds. Spontaneous reactivation of cholinesterase is more rapid
ing workers and in agricultural pesticide applicators have been after inhibition by the carbamates. The therapeutic index, the
published (see References). ratio of the doses that cause severe toxicity or death to those that
Recent clinical observation has also defined an intermediate result in minor intoxication, is larger with carbamates than with
syndrome in severely organophosphate-poisoned patients. This the organophosphorus agents. Although the clinical approach to
syndrome is characterized by neuromuscular transmission failure, carbamate poisoning is similar to that for organophosphates, the
and cardiac failure more typical of nicotinic than muscarinic use of pralidoxime is not recommended.
poisoning. Progressive neuromuscular failure leads to weakness of The carbamates are considered to be nonpersistent pesticides.
the respiratory muscles and eventually to death. The physiologic They exert only a small impact on the environment.
abnormalities are complex but involve a progressive decrement
in neuromuscular junction transmission efficiency. Patients who Botanical Pesticides
develop this intermediate syndrome are at great risk of cardiore-
spiratory failure and may require mechanical ventilation. Because Pesticides derived from natural sources include nicotine, rote-
organophosphorus poisoning frequently occurs in less developed none, and pyrethrum. Nicotine is obtained from the dried leaves
parts of the world where medical resources are very limited, the of Nicotiana tabacum and N rustica. It is rapidly absorbed from
development of the intermediate syndrome is frequently a lethal mucosal surfaces; the free alkaloid, but not the salt, is readily
complication. It is not effectively treated with the usual manage- absorbed from the skin. Nicotine reacts with the acetylcholine
ment protocol for organophosphate pesticide poisoning. receptor of the postsynaptic membrane (sympathetic and para-
sympathetic ganglia, neuromuscular junction), resulting in depo-
2. Environmental toxicology—Organophosphorus pesticides larization of the membrane. Toxic doses cause stimulation rapidly
are not considered to be persistent pesticides. They are relatively followed by blockade of transmission. These actions are described
unstable and break down in the environment as a result of hydro- in Chapter 7. Treatment is directed toward maintenance of vital
lysis and photolysis. As a class they are considered to have a small signs and suppression of convulsions. Nicotine analogs (neonic-
permanent impact on the environment, in spite of their acute otinoids) have been developed for use as agricultural pesticides
effects on organisms. and have been accused of a role in bee colony collapse.
Rotenone (Figure 56–1) is obtained from Derris elliptica,
Carbamate Pesticides D mallaccensis, Lonchocarpus utilis, and L urucu. The oral inges-
tion of rotenone produces gastrointestinal irritation. Conjunctivi-
These compounds (Table 56–4) inhibit acetylcholinesterase by
carbamoylation of the esteratic site. Thus, they possess the toxic tis, dermatitis, pharyngitis, and rhinitis can also occur. Treatment
properties associated with inhibition of this enzyme as described is symptomatic.
Pyrethrum consists of six known insecticidal esters: pyrethrin I
(Figure 56–1), pyrethrin II, cinerin I, cinerin II, jasmolin I, and
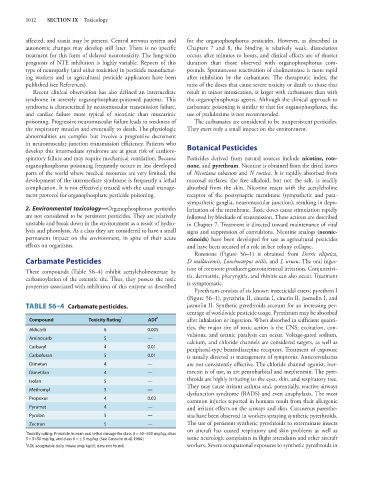
TABLE 56–4 Carbamate pesticides. jasmolin II. Synthetic pyrethroids account for an increasing per-
centage of worldwide pesticide usage. Pyrethrum may be absorbed
Compound Toxicity Rating 1 ADI 2 after inhalation or ingestion. When absorbed in sufficient quanti-
ties, the major site of toxic action is the CNS; excitation, con-
Aldicarb 6 0.005
vulsions, and tetanic paralysis can occur. Voltage-gated sodium,
Aminocarb 5 —
calcium, and chloride channels are considered targets, as well as
Carbaryl 4 0.01
peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors. Treatment of exposure
Carbofuran 5 0.01 is usually directed at management of symptoms. Anticonvulsants
Dimetan 4 — are not consistently effective. The chloride channel agonist, iver-
Dimetilan 4 — mectin is of use, as are pentobarbital and mephenesin. The pyre-
throids are highly irritating to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tree.
Isolan 5 —
They may cause irritant asthma and, potentially, reactive airways
Methomyl 5 —
dysfunction syndrome (RADS) and even anaphylaxis. The most
Propoxur 4 0.02
common injuries reported in humans result from their allergenic
Pyramat 4 — and irritant effects on the airways and skin. Cutaneous paresthe-
Pyrolan 5 — sias have been observed in workers spraying synthetic pyrethroids.
Zectran 5 — The use of persistent synthetic pyrethroids to exterminate insects
on aircraft has caused respiratory and skin problems as well as
1
Toxicity rating: Probable human oral lethal dosage for class 4 = 50−500 mg/kg, class
5 = 5−50 mg/kg, and class 6 = ≤ 5 mg/kg. (See Gosselin et al, 1984.) some neurologic complaints in flight attendants and other aircraft
2 workers. Severe occupational exposures to synthetic pyrethroids in
ADI, acceptable daily intake (mg/kg/d), data not found.