Page 1121 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1121
CHAPTER 62 Drugs Used in the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases 1107
Disease Responsiveness work topically (not systemically) in areas of diseased gastroin-
severity Therapy to therapy testinal mucosa. Up to 80% of unformulated, aqueous 5-ASA is
absorbed from the small intestine and does not reach the distal
Surgery small bowel or colon in appreciable quantities. To overcome the
Natalizumab
Severe Cyclosporine Refractory rapid absorption of 5-ASA from the proximal small intestine, a
TNF antagonists number of formulations have been designed to deliver 5-ASA to
Intravenous corticosteroids various distal segments of the small bowel or the colon. These
include sulfasalazine, olsalazine, balsalazide, and various forms
TNF antagonists of mesalamine.
Oral corticosteroids
Moderate
Methotrexate
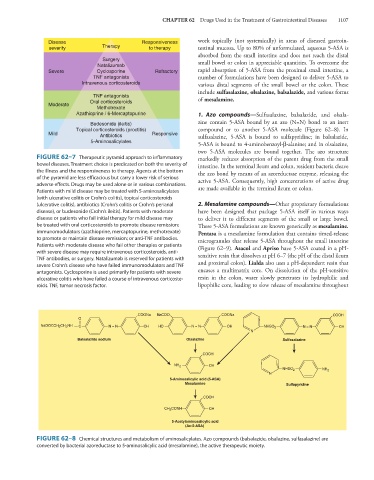
Azathioprine / 6-Mercaptopurine 1. Azo compounds—Sulfasalazine, balsalazide, and olsala-
Budesonide (ileitis) zine contain 5-ASA bound by an azo (N=N) bond to an inert
Topical corticosteroids (proctitis) compound or to another 5-ASA molecule (Figure 62–8). In
Mild Antibiotics Responsive sulfasalazine, 5-ASA is bound to sulfapyridine; in balsalazide,
5-Aminosalicylates
5-ASA is bound to 4-aminobenzoyl-β-alanine; and in olsalazine,
two 5-ASA molecules are bound together. The azo structure
FIGURE 62–7 Therapeutic pyramid approach to inflammatory markedly reduces absorption of the parent drug from the small
bowel diseases. Treatment choice is predicated on both the severity of intestine. In the terminal ileum and colon, resident bacteria cleave
the illness and the responsiveness to therapy. Agents at the bottom the azo bond by means of an azoreductase enzyme, releasing the
of the pyramid are less efficacious but carry a lower risk of serious active 5-ASA. Consequently, high concentrations of active drug
adverse effects. Drugs may be used alone or in various combinations.
Patients with mild disease may be treated with 5-aminosalicylates are made available in the terminal ileum or colon.
(with ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s colitis), topical corticosteroids
(ulcerative colitis), antibiotics (Crohn’s colitis or Crohn’s perianal 2. Mesalamine compounds—Other proprietary formulations
disease), or budesonide (Crohn’s ileitis). Patients with moderate have been designed that package 5-ASA itself in various ways
disease or patients who fail initial therapy for mild disease may to deliver it to different segments of the small or large bowel.
be treated with oral corticosteroids to promote disease remission; These 5-ASA formulations are known generically as mesalamine.
immunomodulators (azathioprine, mercaptopurine, methotrexate) Pentasa is a mesalamine formulation that contains timed-release
to promote or maintain disease remission; or anti-TNF antibodies. microgranules that release 5-ASA throughout the small intestine
Patients with moderate disease who fail other therapies or patients (Figure 62–9). Asacol and Apriso have 5-ASA coated in a pH-
with severe disease may require intravenous corticosteroids, anti-
TNF antibodies, or surgery. Natalizumab is reserved for patients with sensitive resin that dissolves at pH 6–7 (the pH of the distal ileum
severe Crohn’s disease who have failed immunomodulators and TNF and proximal colon). Lialda also uses a pH-dependent resin that
antagonists. Cyclosporine is used primarily for patients with severe encases a multimatrix core. On dissolution of the pH-sensitive
ulcerative colitis who have failed a course of intravenous corticoste- resin in the colon, water slowly penetrates its hydrophilic and
roids. TNF, tumor necrosis factor. lipophilic core, leading to slow release of mesalamine throughout
COONa NaCOO COONa COOH
O
NaOOCCH 2 CH 2 NH C N = N OH HO N = N OH NHSO 2 N = N OH
N
Balsalazide sodium Olsalazine Sulfasalazine
COOH
NH 2 OH
NHSO 2 NH 2
N
5-Aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA)
Mesalamine Sulfapyridine
COOH
CH 2 CONH OH
5-Acetylaminosalicylic acid
(Ac-5-ASA)
FIGURE 62–8 Chemical structures and metabolism of aminosalicylates. Azo compounds (balsalazide, olsalazine, sulfasalazine) are
converted by bacterial azoreductase to 5-aminosalicylic acid (mesalamine), the active therapeutic moiety.