Page 1173 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1173
CHAPTER 66 Important Drug Interactions & Their Mechanisms 1159
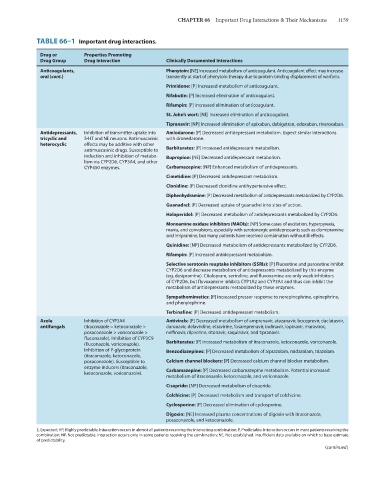
TABLE 66–1 Important drug interactions.
Drug or Properties Promoting
Drug Group Drug Interaction Clinically Documented Interactions
Anticoagulants, Phenytoin: [NE] Increased metabolism of anticoagulant. Anticoagulant effect may increase
oral (cont.) transiently at start of phenytoin therapy due to protein-binding displacement of warfarin.
Primidone: [P] Increased metabolism of anticoagulant.
Rifabutin: [P] Increased elimination of anticoagulant.
Rifampin: [P] Increased elimination of anticoagulant.
St. John’s wort: [NE] Increased elimination of anticoagulant.
Tipranavir: [NP] Increased elimination of apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, rivaroxaban.
Antidepressants, Inhibition of transmitter uptake into Amiodarone: [P] Decreased antidepressant metabolism. Expect similar interactions
tricyclic and 5-HT and NE neurons. Antimuscarinic with dronedarone.
heterocyclic effects may be additive with other
antimuscarinic drugs. Susceptible to Barbiturates: [P] Increased antidepressant metabolism.
induction and inhibition of metabo- Bupropion: [NE] Decreased antidepressant metabolism.
lism via CYP2D6, CYP3A4, and other
CYP450 enzymes. Carbamazepine: [NP] Enhanced metabolism of antidepressants.
Cimetidine: [P] Decreased antidepressant metabolism.
Clonidine: [P] Decreased clonidine antihypertensive effect.
Diphenhydramine: [P] Decreased metabolism of antidepressants metabolized by CYP2D6.
Guanadrel: [P] Decreased uptake of guanadrel into sites of action.
Haloperidol: [P] Decreased metabolism of antidepressants metabolized by CYP2D6.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): [NP] Some cases of excitation, hyperpyrexia,
mania, and convulsions, especially with serotonergic antidepressants such as clomipramine
and imipramine, but many patients have received combination without ill effects.
Quinidine: [NP] Decreased metabolism of antidepressants metabolized by CYP2D6.
Rifampin: [P] Increased antidepressant metabolism.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): [P] Fluoxetine and paroxetine inhibit
CYP2D6 and decrease metabolism of antidepressants metabolized by this enzyme
(eg, desipramine). Citalopram, sertraline, and fluvoxamine are only weak inhibitors
of CYP2D6, but fluvoxamine inhibits CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 and thus can inhibit the
metabolism of antidepressants metabolized by these enzymes.
Sympathomimetics: [P] Increased pressor response to norepinephrine, epinephrine,
and phenylephrine.
Terbinafine: [P] Decreased antidepressant metabolism.
Azole Inhibition of CYP3A4 Antivirals: [P] Decreased metabolism of amprenavir, atazanavir, boceprevir, daclatasvir,
antifungals (itraconazole = ketoconazole > darunavir, delavirdine, etravirine, fosamprenavir, indinavir, lopinavir, maraviroc,
posaconazole > voriconazole > nelfinavir, rilpivirine, ritonavir, saquinavir, and tipranavir.
fluconazole). Inhibition of CYP2C9
(fluconazole, voriconazole). Barbiturates: [P] Increased metabolism of itraconazole, ketoconazole, voriconazole.
Inhibition of P-glycoprotein Benzodiazepines: [P] Decreased metabolism of alprazolam, midazolam, triazolam.
(itraconazole, ketoconazole,
posaconazole). Susceptible to Calcium channel blockers: [P] Decreased calcium channel blocker metabolism.
enzyme inducers (itraconazole, Carbamazepine: [P] Decreased carbamazepine metabolism. Potential increased
ketoconazole, voriconazole).
metabolism of itraconazole, ketoconazole, and voriconazole.
Cisapride: [NP] Decreased metabolism of cisapride.
Colchicine: [P] Decreased metabolism and transport of colchicine.
Cyclosporine: [P] Decreased elimination of cyclosporine.
Digoxin: [NE] Increased plasma concentrations of digoxin with itraconazole,
posaconazole, and ketoconazole.
E, Expected; HP, Highly predictable. Interaction occurs in almost all patients receiving the interacting combination; P, Predictable. Interaction occurs in most patients receiving the
combination; NP, Not predictable. Interaction occurs only in some patients receiving the combination; NE, Not established. Insufficient data available on which to base estimate
of predictability.
(continued )