Page 1175 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1175
CHAPTER 66 Important Drug Interactions & Their Mechanisms 1161
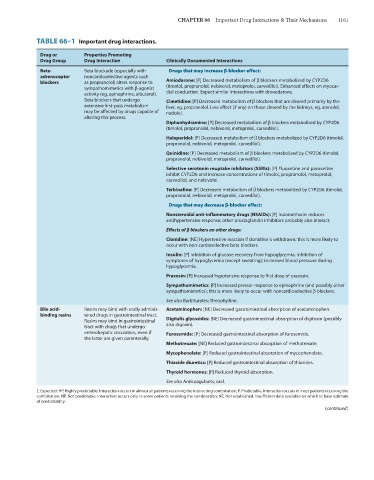
TABLE 66–1 Important drug interactions.
Drug or Properties Promoting
Drug Group Drug Interaction Clinically Documented Interactions
Beta- Beta blockade (especially with Drugs that may increase β-blocker effect:
adrenoceptor noncardioselective agents such
blockers as propranolol) alters response to Amiodarone: [P] Decreased metabolism of β blockers metabolized by CYP2D6
sympathomimetics with β-agonist (timolol, propranolol, nebivolol, metoprolol, carvedilol). Enhanced effects on myocar-
activity (eg, epinephrine, albuterol). dial conduction. Expect similar interactions with dronedarone.
Beta blockers that undergo Cimetidine: [P] Decreased metabolism of β blockers that are cleared primarily by the
extensive first-pass metabolism liver, eg, propranolol. Less effect (if any) on those cleared by the kidneys, eg, atenolol,
may be affected by drugs capable of nadolol.
altering this process.
Diphenhydramine: [P] Decreased metabolism of β blockers metabolized by CYP2D6
(timolol, propranolol, nebivolol, metoprolol, carvedilol).
Haloperidol: [P] Decreased metabolism of β blockers metabolized by CYP2D6 (timolol,
propranolol, nebivolol, metoprolol, carvedilol).
Quinidine: [P] Decreased metabolism of β blockers metabolized by CYP2D6 (timolol,
propranolol, nebivolol, metoprolol, carvedilol).
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): [P] Fluoxetine and paroxetine
inhibit CYP2D6 and increase concentrations of timolol, propranolol, metoprolol,
carvedilol, and nebivolol.
Terbinafine: [P] Decreased metabolism of β blockers metabolized by CYP2D6 (timolol,
propranolol, nebivolol, metoprolol, carvedilol).
Drugs that may decrease β-blocker effect:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): [P] Indomethacin reduces
antihypertensive response; other prostaglandin inhibitors probably also interact.
Effects of β blockers on other drugs:
Clonidine: [NE] Hypertensive reaction if clonidine is withdrawn; this is more likely to
occur with non-cardioselective beta blockers.
Insulin: [P] Inhibition of glucose recovery from hypoglycemia; inhibition of
symptoms of hypoglycemia (except sweating); increased blood pressure during
hypoglycemia.
Prazosin: [P] Increased hypotensive response to first dose of prazosin.
Sympathomimetics: [P] Increased pressor response to epinephrine (and possibly other
sympathomimetics); this is more likely to occur with noncardioselective β blockers.
See also Barbiturates; Theophylline.
Bile acid- Resins may bind with orally adminis- Acetaminophen: [NE] Decreased gastrointestinal absorption of acetaminophen.
binding resins tered drugs in gastrointestinal tract.
Resins may bind in gastrointestinal Digitalis glycosides: [NE] Decreased gastrointestinal absorption of digitoxin (possibly
tract with drugs that undergo also digoxin).
enterohepatic circulation, even if Furosemide: [P] Decreased gastrointestinal absorption of furosemide.
the latter are given parenterally.
Methotrexate: [NE] Reduced gastrointestinal absorption of methotrexate.
Mycophenolate: [P] Reduced gastrointestinal absorption of mycophenolate.
Thiazide diuretics: [P] Reduced gastrointestinal absorption of thiazides.
Thyroid hormones: [P] Reduced thyroid absorption.
See also Anticoagulants, oral.
E, Expected; HP, Highly predictable. Interaction occurs in almost all patients receiving the interacting combination; P, Predictable. Interaction occurs in most patients receiving the
combination; NP, Not predictable. Interaction occurs only in some patients receiving the combination; NE, Not established. Insufficient data available on which to base estimate
of predictability.
(continued )