Page 1171 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1171
CHAPTER 66 Important Drug Interactions & Their Mechanisms 1157
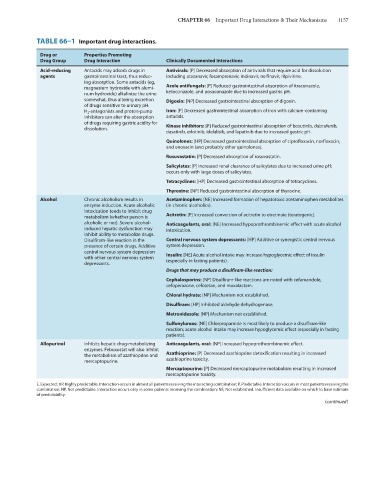
TABLE 66–1 Important drug interactions.
Drug or Properties Promoting
Drug Group Drug Interaction Clinically Documented Interactions
Acid-reducing Antacids may adsorb drugs in Antivirals: [P] Decreased absorption of antivirals that require acid for dissolution
agents gastrointestinal tract, thus reduc- including atazanavir, fosamprenavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, rilpivirine.
ing absorption. Some antacids (eg,
magnesium hydroxide with alumi- Azole antifungals: [P] Reduced gastrointestinal absorption of itraconazole,
num hydroxide) alkalinize the urine ketoconazole, and posaconazole due to increased gastric pH.
somewhat, thus altering excretion Digoxin: [NP] Decreased gastrointestinal absorption of digoxin.
of drugs sensitive to urinary pH.
H 2 -antagonists and proton-pump Iron: [P] Decreased gastrointestinal absorption of iron with calcium-containing
inhibitors can alter the absorption antacids.
of drugs requiring gastric acidity for Kinase inhibitors: [P] Reduced gastrointestinal absorption of bosutinib, dabrafenib,
dissolution.
dasatinib, erlotinib, idelalisib, and lapatinib due to increased gastric pH.
Quinolones: [HP] Decreased gastrointestinal absorption of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin,
and enoxacin (and probably other quinolones).
Rosuvastatin: [P] Decreased absorption of rosuvastatin.
Salicylates: [P] Increased renal clearance of salicylates due to increased urine pH;
occurs only with large doses of salicylates.
Tetracyclines: [HP] Decreased gastrointestinal absorption of tetracyclines.
Thyroxine: [NP] Reduced gastrointestinal absorption of thyroxine.
Alcohol Chronic alcoholism results in Acetaminophen: [NE] Increased formation of hepatotoxic acetaminophen metabolites
enzyme induction. Acute alcoholic (in chronic alcoholics).
intoxication tends to inhibit drug
metabolism (whether person is Acitretin: [P] Increased conversion of acitretin to etretinate (teratogenic).
alcoholic or not). Severe alcohol- Anticoagulants, oral: [NE] Increased hypoprothrombinemic effect with acute alcohol
induced hepatic dysfunction may intoxication.
inhibit ability to metabolize drugs.
Disulfiram-like reaction in the Central nervous system depressants: [HP] Additive or synergistic central nervous
presence of certain drugs. Additive system depression.
central nervous system depression
with other central nervous system Insulin: [NE] Acute alcohol intake may increase hypoglycemic effect of insulin
(especially in fasting patients).
depressants.
Drugs that may produce a disulfiram-like reaction:
Cephalosporins: [NP] Disulfiram-like reactions are noted with cefamandole,
cefoperazone, cefotetan, and moxalactam.
Chloral hydrate: [NP] Mechanism not established.
Disulfiram: [HP] Inhibited aldehyde dehydrogenase.
Metronidazole: [NP] Mechanism not established.
Sulfonylureas: [NE] Chlorpropamide is most likely to produce a disulfiram-like
reaction; acute alcohol intake may increase hypoglycemic effect (especially in fasting
patients).
Allopurinol Inhibits hepatic drug-metabolizing Anticoagulants, oral: [NP] Increased hypoprothrombinemic effect.
enzymes. Febuxostat will also inhibit
the metabolism of azathioprine and Azathioprine: [P] Decreased azathioprine detoxification resulting in increased
mercaptopurine. azathioprine toxicity.
Mercaptopurine: [P] Decreased mercaptopurine metabolism resulting in increased
mercaptopurine toxicity.
E, Expected; HP, Highly predictable. Interaction occurs in almost all patients receiving the interacting combination; P, Predictable. Interaction occurs in most patients receiving the
combination; NP, Not predictable. Interaction occurs only in some patients receiving the combination; NE, Not established. Insufficient data available on which to base estimate
of predictability.
(continued )