Page 354 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 354
340 SECTION IV Drugs with Important Actions on Smooth Muscle
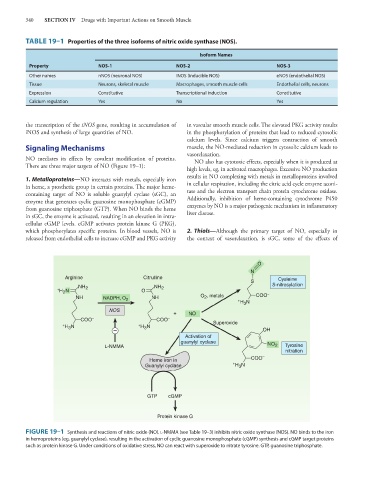
TABLE 19–1 Properties of the three isoforms of nitric oxide synthase (NOS).
Isoform Names
Property NOS-1 NOS-2 NOS-3
Other names nNOS (neuronal NOS) iNOS (inducible NOS) eNOS (endothelial NOS)
Tissue Neurons, skeletal muscle Macrophages, smooth muscle cells Endothelial cells, neurons
Expression Constitutive Transcriptional induction Constitutive
Calcium regulation Yes No Yes
the transcription of the iNOS gene, resulting in accumulation of in vascular smooth muscle cells. The elevated PKG activity results
iNOS and synthesis of large quantities of NO. in the phosphorylation of proteins that lead to reduced cytosolic
calcium levels. Since calcium triggers contraction of smooth
Signaling Mechanisms muscle, the NO-mediated reduction in cytosolic calcium leads to
vasorelaxation.
NO mediates its effects by covalent modification of proteins. NO also has cytotoxic effects, especially when it is produced at
There are three major targets of NO (Figure 19–1):
high levels, eg, in activated macrophages. Excessive NO production
results in NO complexing with metals in metalloproteins involved
1. Metalloproteins—NO interacts with metals, especially iron
in heme, a prosthetic group in certain proteins. The major heme- in cellular respiration, including the citric acid cycle enzyme aconi-
containing target of NO is soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC), an tase and the electron transport chain protein cytochrome oxidase.
enzyme that generates cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) Additionally, inhibition of heme-containing cytochrome P450
from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). When NO binds the heme enzymes by NO is a major pathogenic mechanism in inflammatory
in sGC, the enzyme is activated, resulting in an elevation in intra- liver disease.
cellular cGMP levels. cGMP activates protein kinase G (PKG),
which phosphorylates specific proteins. In blood vessels, NO is 2. Thiols—Although the primary target of NO, especially in
released from endothelial cells to increase cGMP and PKG activity the context of vasorelaxation, is sGC, some of the effects of
O
N
Arginine Citrulline Cysteine
S
NH NH S-nitrosylation
+ H N 2 O 2
2
NH NADPH, O 2 NH O , metals + H N COO –
2
3
NOS
+ NO
COO – COO –
+ H N + H N Superoxide OH
3
3
Activation of
guanylyl cyclase NO
L-NMMA 2 Tyrosine
nitration
Heme iron in COO –
Guanylyl cyclase + H N
3
GTP cGMP
Protein kinase G
FIGURE 19–1 Synthesis and reactions of nitric oxide (NO). l-NMMA (see Table 19–3) inhibits nitric oxide synthase (NOS). NO binds to the iron
in hemoproteins (eg, guanylyl cyclase), resulting in the activation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) synthesis and cGMP target proteins
such as protein kinase G. Under conditions of oxidative stress, NO can react with superoxide to nitrate tyrosine. GTP, guanosine triphosphate.