Page 382 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 382
368 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
ORGANIZATION OF THE CNS functions in the CNS. Astrocytes are the most abundant cell in
the brain and play homeostatic support roles, including providing
The CNS is composed of the brain and spinal cord and is respon- metabolic nutrients to neurons and maintaining extracellular ion
sible for integrating sensory information and generating motor concentrations. In addition, astrocyte processes are closely associated
output and other behaviors needed to successfully interact with with neuronal synapses where they are involved in the removal and
the environment and enhance species survival. The human brain recycling of neurotransmitters after release and play increasingly
contains about 100 billion interconnected neurons surrounded by appreciated roles in regulating neurotransmission (see below).
various supporting glial cells. Throughout the CNS, neurons are Oligodendrocytes are cells that wrap around the axons of projec-
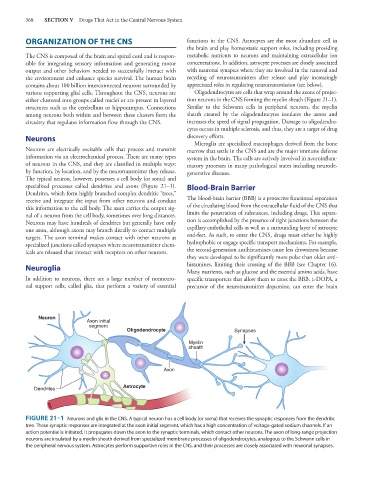
either clustered into groups called nuclei or are present in layered tion neurons in the CNS forming the myelin sheath (Figure 21–1).
structures such as the cerebellum or hippocampus. Connections Similar to the Schwann cells in peripheral neurons, the myelin
among neurons both within and between these clusters form the sheath created by the oligodendrocytes insulates the axons and
circuitry that regulates information flow through the CNS. increases the speed of signal propagation. Damage to oligodendro-
cytes occurs in multiple sclerosis, and thus, they are a target of drug
Neurons discovery efforts.
Microglia are specialized macrophages derived from the bone
Neurons are electrically excitable cells that process and transmit marrow that settle in the CNS and are the major immune defense
information via an electrochemical process. There are many types system in the brain. The cells are actively involved in neuroinflam-
of neurons in the CNS, and they are classified in multiple ways: matory processes in many pathological states including neurode-
by function, by location, and by the neurotransmitter they release. generative diseases.
The typical neuron, however, possesses a cell body (or soma) and
specialized processes called dendrites and axons (Figure 21–1). Blood-Brain Barrier
Dendrites, which form highly branched complex dendritic “trees,”
receive and integrate the input from other neurons and conduct The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a protective functional separation
this information to the cell body. The axon carries the output sig- of the circulating blood from the extracellular fluid of the CNS that
nal of a neuron from the cell body, sometimes over long distances. limits the penetration of substances, including drugs. This separa-
Neurons may have hundreds of dendrites but generally have only tion is accomplished by the presence of tight junctions between the
one axon, although axons may branch distally to contact multiple capillary endothelial cells as well as a surrounding layer of astrocyte
targets. The axon terminal makes contact with other neurons at end-feet. As such, to enter the CNS, drugs must either be highly
specialized junctions called synapses where neurotransmitter chem- hydrophobic or engage specific transport mechanisms. For example,
icals are released that interact with receptors on other neurons. the second-generation antihistamines cause less drowsiness because
they were developed to be significantly more polar than older anti-
Neuroglia histamines, limiting their crossing of the BBB (see Chapter 16).
Many nutrients, such as glucose and the essential amino acids, have
In addition to neurons, there are a large number of nonneuro- specific transporters that allow them to cross the BBB. l-DOPA, a
nal support cells, called glia, that perform a variety of essential precursor of the neurotransmitter dopamine, can enter the brain
Neuron
Axon initial
segment
Oligodendrocyte Synapses
Myelin
sheath
Axon
Dendrites Astrocyte
FIGURE 21–1 Neurons and glia in the CNS. A typical neuron has a cell body (or soma) that receives the synaptic responses from the dendritic
tree. These synaptic responses are integrated at the axon initial segment, which has a high concentration of voltage-gated sodium channels. If an
action potential is initiated, it propagates down the axon to the synaptic terminals, which contact other neurons. The axon of long-range projection
neurons are insulated by a myelin sheath derived from specialized membrane processes of oligodendrocytes, analogous to the Schwann cells in
the peripheral nervous system. Astrocytes perform supportive roles in the CNS, and their processes are closely associated with neuronal synapses.