Page 564 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 564
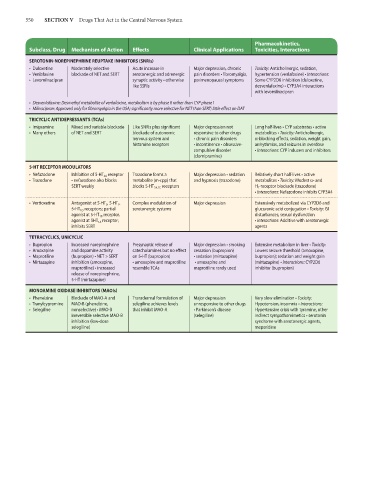
550 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
Pharmacokinetics,
Subclass, Drug Mechanism of Action Effects Clinical Applications Toxicities, Interactions
SEROTONIN-NOREPINEPHRINE REUPTAKE INHIBITORS (SNRIs)
• Duloxetine Moderately selective Acute increase in Major depression, chronic Toxicity: Anticholinergic, sedation,
• Venlafaxine blockade of NET and SERT serotonergic and adrenergic pain disorders • fibromyalgia, hypertension (venlafaxine) • Interactions:
• Levomilnacipran synaptic activity • otherwise perimenopausal symptoms Some CYP2D6 inhibition (duloxetine,
like SSRIs desvenlafaxine) • CYP3A4 interactions
with levomilnacipran
• Desvenlafaxine: Desmethyl metabolite of venlafaxine, metabolism is by phase II rather than CYP phase I
• Milnacipran: Approved only for fibromyalgia in the USA; significantly more selective for NET than SERT; little effect on DAT
TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANTS (TCAs)
• Imipramine Mixed and variable blockade Like SNRIs plus significant Major depression not Long half-lives • CYP substrates • active
• Many others of NET and SERT blockade of autonomic responsive to other drugs metabolites • Toxicity: Anticholinergic,
nervous system and • chronic pain disorders α-blocking effects, sedation, weight gain,
histamine receptors • incontinence • obsessive- arrhythmias, and seizures in overdose
compulsive disorder • Interactions: CYP inducers and inhibitors
(clomipramine)
5-HT RECEPTOR MODULATORS
• Nefazodone Inhibition of 5-HT 2A receptor Trazodone forms a Major depression • sedation Relatively short half-lives • active
• Trazodone • nefazodone also blocks metabolite (m-cpp) that and hypnosis (trazodone) metabolites • Toxicity: Modest α- and
SERT weakly blocks 5-HT 2A,2C receptors H 1 -receptor blockade (trazodone)
• Interactions: Nefazodone inhibits CYP3A4
• Vortioxetine Antagonist at 5-HT 3 , 5-HT 7 , Complex modulation of Major depression Extensively metabolized via CYP2D6 and
5-HT 1D receptors; partial serotonergic systems glucuronic acid conjugation • Toxicity: GI
agonist at 5-HT 1B receptor, disturbances, sexual dysfunction
agonist at 5HT 1A receptor; • Interactions: Additive with serotonergic
inhibits SERT agents
TETRACYCLICS, UNICYCLIC
• Bupropion Increased norepinephrine Presynaptic release of Major depression • smoking Extensive metabolism in liver • Toxicity:
• Amoxapine and dopamine activity catecholamines but no effect cessation (bupropion) Lowers seizure threshold (amoxapine,
• Maprotiline (bupropion) • NET > SERT on 5-HT (bupropion) • sedation (mirtazapine) bupropion); sedation and weight gain
• Mirtazapine inhibition (amoxapine, • amoxapine and maprotiline • amoxapine and (mirtazapine) • Interactions: CYP2D6
maprotiline) • increased resemble TCAs maprotiline rarely used inhibitor (bupropion)
release of norepinephrine,
5-HT (mirtazapine)
MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITORS (MAOIs)
• Phenelzine Blockade of MAO-A and Transdermal formulation of Major depression Very slow elimination • Toxicity:
• Tranylcypromine MAO-B (phenelzine, selegiline achieves levels unresponsive to other drugs Hypotension, insomnia • Interactions:
• Selegiline nonselective) • MAO-B that inhibit MAO-A • Parkinson’s disease Hypertensive crisis with tyramine, other
irreversible selective MAO-B (selegiline) indirect sympathomimetics • serotonin
inhibition (low-dose syndrome with serotonergic agents,
selegiline) meperidine