Page 569 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 569
CHAPTER 31 Opioid Agonists & Antagonists 555
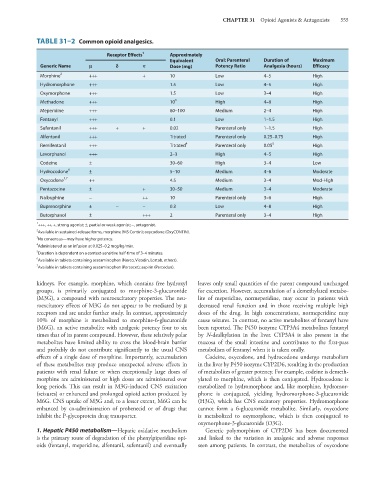
TABLE 31–2 Common opioid analgesics.
Receptor Effects 1 Approximately
Equivalent Oral: Parenteral Duration of Maximum
Generic Name l c j Dose (mg) Potency Ratio Analgesia (hours) Efficacy
Morphine 2 +++ + 10 Low 4–5 High
Hydromorphone +++ 1.5 Low 4–5 High
Oxymorphone +++ 1.5 Low 3–4 High
Methadone +++ 10 3 High 4–6 High
Meperidine +++ 60–100 Medium 2–4 High
Fentanyl +++ 0.1 Low 1–1.5 High
Sufentanil +++ + + 0.02 Parenteral only 1–1.5 High
Alfentanil +++ Titrated Parenteral only 0.25–0.75 High
Remifentanil +++ Titrated 4 Parenteral only 0.05 5 High
Levorphanol +++ 2–3 High 4–5 High
Codeine ± 30–60 High 3–4 Low
Hydrocodone 6 ± 5–10 Medium 4–6 Moderate
Oxycodone 2,7 ++ 4.5 Medium 3–4 Mod-High
Pentazocine ± + 30–50 Medium 3–4 Moderate
Nalbuphine - ++ 10 Parenteral only 3–6 High
Buprenorphine ± - - 0.3 Low 4–8 High
Butorphanol ± +++ 2 Parenteral only 3–4 High
1 +++, ++, +, strong agonist; ±, partial or weak agonist; -, antagonist.
2
Available in sustained-release forms, morphine (MS Contin); oxycodone (OxyCONTIN).
3 No consensus—may have higher potency.
4
Administered as an infusion at 0.025–0.2 mcg/kg/min.
5 Duration is dependent on a context-sensitive half-time of 3–4 minutes.
6
Available in tablets containing acetaminophen (Norco, Vicodin, Lortab, others).
7 Available in tablets containing acetaminophen (Percocet); aspirin (Percodan).
kidneys. For example, morphine, which contains free hydroxyl leaves only small quantities of the parent compound unchanged
groups, is primarily conjugated to morphine-3-glucuronide for excretion. However, accumulation of a demethylated metabo-
(M3G), a compound with neuroexcitatory properties. The neu- lite of meperidine, normeperidine, may occur in patients with
roexcitatory effects of M3G do not appear to be mediated by μ decreased renal function and in those receiving multiple high
receptors and are under further study. In contrast, approximately doses of the drug. In high concentrations, normeperidine may
10% of morphine is metabolized to morphine-6-glucuronide cause seizures. In contrast, no active metabolites of fentanyl have
(M6G), an active metabolite with analgesic potency four to six been reported. The P450 isozyme CYP3A4 metabolizes fentanyl
times that of its parent compound. However, these relatively polar by N-dealkylation in the liver. CYP3A4 is also present in the
metabolites have limited ability to cross the blood-brain barrier mucosa of the small intestine and contributes to the first-pass
and probably do not contribute significantly to the usual CNS metabolism of fentanyl when it is taken orally.
effects of a single dose of morphine. Importantly, accumulation Codeine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone undergo metabolism
of these metabolites may produce unexpected adverse effects in in the liver by P450 isozyme CYP2D6, resulting in the production
patients with renal failure or when exceptionally large doses of of metabolites of greater potency. For example, codeine is demeth-
morphine are administered or high doses are administered over ylated to morphine, which is then conjugated. Hydrocodone is
long periods. This can result in M3G-induced CNS excitation metabolized to hydromorphone and, like morphine, hydromor-
(seizures) or enhanced and prolonged opioid action produced by phone is conjugated, yielding hydromorphone-3-glucuronide
M6G. CNS uptake of M3G and, to a lesser extent, M6G can be (H3G), which has CNS excitatory properties. Hydromorphone
enhanced by co-administration of probenecid or of drugs that cannot form a 6-glucuronide metabolite. Similarly, oxycodone
inhibit the P-glycoprotein drug transporter. is metabolized to oxymorphone, which is then conjugated to
oxymorphone-3-glucuronide (O3G).
1. Hepatic P450 metabolism—Hepatic oxidative metabolism Genetic polymorphism of CYP2D6 has been documented
is the primary route of degradation of the phenylpiperidine opi- and linked to the variation in analgesic and adverse responses
oids (fentanyl, meperidine, alfentanil, sufentanil) and eventually seen among patients. In contrast, the metabolites of oxycodone