Page 571 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 571
CHAPTER 31 Opioid Agonists & Antagonists 557
Pain
stimulus Periphery
MOR
Primary
afferent
fiber
–
MOR
Glutamate α 2
K +
Neuropeptide
– –
Ca 2+
Dorsal horn
spinal cord
MOR
NMDA +
AMPA
NK1
K +
Secondary
afferent
neuron
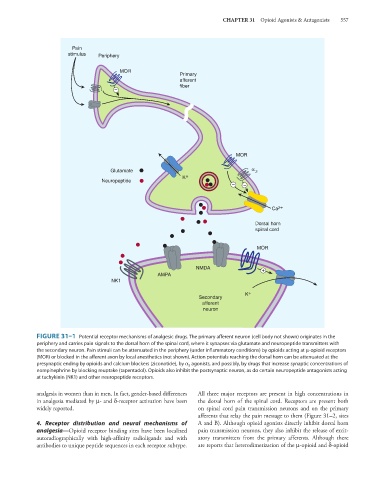
FIGURE 31–1 Potential receptor mechanisms of analgesic drugs. The primary afferent neuron (cell body not shown) originates in the
periphery and carries pain signals to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, where it synapses via glutamate and neuropeptide transmitters with
the secondary neuron. Pain stimuli can be attenuated in the periphery (under inflammatory conditions) by opioids acting at μ-opioid receptors
(MOR) or blocked in the afferent axon by local anesthetics (not shown). Action potentials reaching the dorsal horn can be attenuated at the
presynaptic ending by opioids and calcium blockers (ziconotide), by α 2 agonists, and possibly, by drugs that increase synaptic concentrations of
norepinephrine by blocking reuptake (tapentadol). Opioids also inhibit the postsynaptic neuron, as do certain neuropeptide antagonists acting
at tachykinin (NK1) and other neuropeptide receptors.
analgesia in women than in men. In fact, gender-based differences All three major receptors are present in high concentrations in
in analgesia mediated by μ- and δ-receptor activation have been the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Receptors are present both
widely reported. on spinal cord pain transmission neurons and on the primary
afferents that relay the pain message to them (Figure 31–2, sites
4. Receptor distribution and neural mechanisms of A and B). Although opioid agonists directly inhibit dorsal horn
analgesia—Opioid receptor binding sites have been localized pain transmission neurons, they also inhibit the release of excit-
autoradiographically with high-affinity radioligands and with atory transmitters from the primary afferents. Although there
antibodies to unique peptide sequences in each receptor subtype. are reports that heterodimerization of the μ-opioid and δ-opioid