Page 629 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 629
CHAPTER 34 Drugs Used in Disorders of Coagulation 615
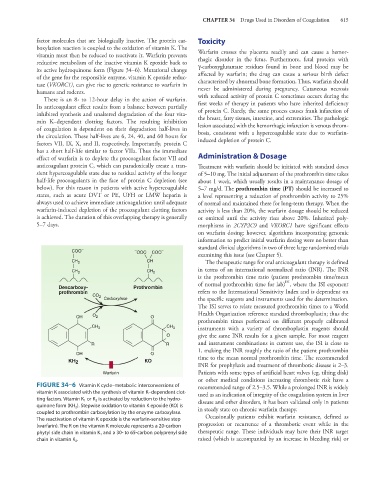
factor molecules that are biologically inactive. The protein car- Toxicity
boxylation reaction is coupled to the oxidation of vitamin K. The
vitamin must then be reduced to reactivate it. Warfarin prevents Warfarin crosses the placenta readily and can cause a hemor-
reductive metabolism of the inactive vitamin K epoxide back to rhagic disorder in the fetus. Furthermore, fetal proteins with
its active hydroquinone form (Figure 34–6). Mutational change γ-carboxyglutamate residues found in bone and blood may be
of the gene for the responsible enzyme, vitamin K epoxide reduc- affected by warfarin; the drug can cause a serious birth defect
tase (VKORC1), can give rise to genetic resistance to warfarin in characterized by abnormal bone formation. Thus, warfarin should
humans and rodents. never be administered during pregnancy. Cutaneous necrosis
There is an 8- to 12-hour delay in the action of warfarin. with reduced activity of protein C sometimes occurs during the
Its anticoagulant effect results from a balance between partially first weeks of therapy in patients who have inherited deficiency
inhibited synthesis and unaltered degradation of the four vita- of protein C. Rarely, the same process causes frank infarction of
min K–dependent clotting factors. The resulting inhibition the breast, fatty tissues, intestine, and extremities. The pathologic
of coagulation is dependent on their degradation half-lives in lesion associated with the hemorrhagic infarction is venous throm-
the circulation. These half-lives are 6, 24, 40, and 60 hours for bosis, consistent with a hypercoagulable state due to warfarin-
factors VII, IX, X, and II, respectively. Importantly, protein C induced depletion of protein C.
has a short half-life similar to factor VIIa. Thus the immediate
effect of warfarin is to deplete the procoagulant factor VII and Administration & Dosage
anticoagulant protein C, which can paradoxically create a tran- Treatment with warfarin should be initiated with standard doses
sient hypercoagulable state due to residual activity of the longer of 5–10 mg. The initial adjustment of the prothrombin time takes
half-life procoagulants in the face of protein C depletion (see about 1 week, which usually results in a maintenance dosage of
below). For this reason in patients with active hypercoagulable 5–7 mg/d. The prothrombin time (PT) should be increased to
states, such as acute DVT or PE, UFH or LMW heparin is a level representing a reduction of prothrombin activity to 25%
always used to achieve immediate anticoagulation until adequate of normal and maintained there for long-term therapy. When the
warfarin-induced depletion of the procoagulant clotting factors activity is less than 20%, the warfarin dosage should be reduced
is achieved. The duration of this overlapping therapy is generally or omitted until the activity rises above 20%. Inherited poly-
5–7 days. morphisms in 2CYP2C9 and VKORC1 have significant effects
on warfarin dosing; however, algorithms incorporating genomic
information to predict initial warfarin dosing were no better than
standard clinical algorithms in two of three large randomized trials
–
COO – OOC COO –
examining this issue (see Chapter 5).
CH 2 CH The therapeutic range for oral anticoagulant therapy is defined
CH 2 CH 2 in terms of an international normalized ratio (INR). The INR
is the prothrombin time ratio (patient prothrombin time/mean
ISI
of normal prothrombin time for lab) , where the ISI exponent
Descarboxy- Prothrombin
prothrombin refers to the International Sensitivity Index and is dependent on
CO 2 Carboxylase the specific reagents and instruments used for the determination.
The ISI serves to relate measured prothrombin times to a World
OH O 2 O Health Organization reference standard thromboplastin; thus the
prothrombin times performed on different properly calibrated
CH 3 CH 3 instruments with a variety of thromboplastin reagents should
O give the same INR results for a given sample. For most reagent
R R and instrument combinations in current use, the ISI is close to
1, making the INR roughly the ratio of the patient prothrombin
OH O
KH 2 KO time to the mean normal prothrombin time. The recommended
INR for prophylaxis and treatment of thrombotic disease is 2–3.
Warfarin Patients with some types of artificial heart valves (eg, tilting disk)
or other medical conditions increasing thrombotic risk have a
FIGURE 34–6 Vitamin K cycle–metabolic interconversions of recommended range of 2.5–3.5. While a prolonged INR is widely
vitamin K associated with the synthesis of vitamin K–dependent clot- used as an indication of integrity of the coagulation system in liver
ting factors. Vitamin K 1 or K 2 is activated by reduction to the hydro- disease and other disorders, it has been validated only in patients
quinone form (KH 2 ). Stepwise oxidation to vitamin K epoxide (KO) is
coupled to prothrombin carboxylation by the enzyme carboxylase. in steady state on chronic warfarin therapy.
The reactivation of vitamin K epoxide is the warfarin-sensitive step Occasionally patients exhibit warfarin resistance, defined as
(warfarin). The R on the vitamin K molecule represents a 20-carbon progression or recurrence of a thrombotic event while in the
phytyl side chain in vitamin K 1 and a 30- to 65-carbon polyprenyl side therapeutic range. These individuals may have their INR target
chain in vitamin K 2 . raised (which is accompanied by an increase in bleeding risk) or