Page 624 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 624
610 SECTION VI Drugs Used to Treat Diseases of the Blood, Inflammation, & Gout
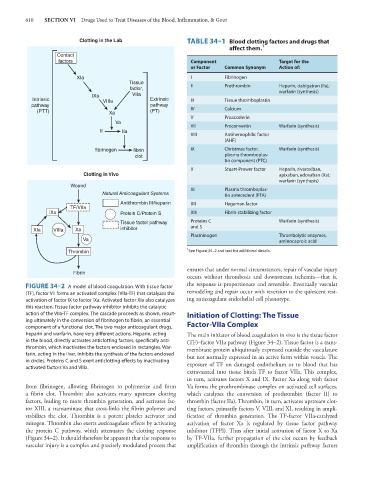
Clotting in the Lab TABLE 34–1 Blood clotting factors and drugs that
affect them. 1
Contact
factors Component Target for the
or Factor Common Synonym Action of:
XIa I Fibrinogen
Tissue
factor, II Prothrombin Heparin, dabigatran (IIa);
warfarin (synthesis)
IXa VIIa
Intrinsic VIIIa Extrinsic III Tissue thromboplastin
pathway pathway IV Calcium
(PTT) Xa (PT)
V Proaccelerin
Va
VII Proconvertin Warfarin (synthesis)
II IIa
VIII Antihemophilic factor
(AHF)
fibrinogen fibrin IX Christmas factor, Warfarin (synthesis)
clot plasma thromboplas-
tin component (PTC)
X Stuart-Prower factor Heparin, rivaroxiban,
Clotting in Vivo apixaban, edoxaban (Xa);
warfarin (synthesis)
Wound
XI Plasma thromboplas-
Natural Anticoagulant Systems tin antecedent (PTA)
Antithrombin III/heparin XII Hageman factor
TF/VIIa
IXa Protein C/Protein S XIII Fibrin-stabilizing factor
Tissue factor pathway Proteins C Warfarin (synthesis)
XIa VIIIa Xa inhibitor and S
Plasminogen Thrombolytic enzymes,
Va aminocaproic acid
1
Thrombin See Figure 34–2 and text for additional details.
ensures that under normal circumstances, repair of vascular injury
Fibrin
occurs without thrombosis and downstream ischemia—that is,
the response is proportionate and reversible. Eventually vascular
FIGURE 34–2 A model of blood coagulation. With tissue factor
(TF), factor VII forms an activated complex (VIIa-TF) that catalyzes the remodeling and repair occur with reversion to the quiescent rest-
activation of factor IX to factor IXa. Activated factor XIa also catalyzes ing anticoagulant endothelial cell phenotype.
this reaction. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor inhibits the catalytic
action of the VIIa-TF complex. The cascade proceeds as shown, result- Initiation of Clotting: The Tissue
ing ultimately in the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, an essential
component of a functional clot. The two major anticoagulant drugs, Factor-VIIa Complex
heparin and warfarin, have very different actions. Heparin, acting The main initiator of blood coagulation in vivo is the tissue factor
in the blood, directly activates anticlotting factors, specifically anti- (TF)–factor VIIa pathway (Figure 34–2). Tissue factor is a trans-
thrombin, which inactivates the factors enclosed in rectangles. War- membrane protein ubiquitously expressed outside the vasculature
farin, acting in the liver, inhibits the synthesis of the factors enclosed but not normally expressed in an active form within vessels. The
in circles. Proteins C and S exert anticlotting effects by inactivating exposure of TF on damaged endothelium or to blood that has
activated factors Va and VIIIa.
extravasated into tissue binds TF to factor VIIa. This complex,
in turn, activates factors X and IX. Factor Xa along with factor
from fibrinogen, allowing fibrinogen to polymerize and form Va forms the prothrombinase complex on activated cell surfaces,
a fibrin clot. Thrombin also activates many upstream clotting which catalyzes the conversion of prothrombin (factor II) to
factors, leading to more thrombin generation, and activates fac- thrombin (factor IIa). Thrombin, in turn, activates upstream clot-
tor XIII, a transaminase that cross-links the fibrin polymer and ting factors, primarily factors V, VIII, and XI, resulting in ampli-
stabilizes the clot. Thrombin is a potent platelet activator and fication of thrombin generation. The TF-factor VIIa-catalyzed
mitogen. Thrombin also exerts anticoagulant effects by activating activation of factor Xa is regulated by tissue factor pathway
the protein C pathway, which attenuates the clotting response inhibitor (TFPI). Thus after initial activation of factor X to Xa
(Figure 34–2). It should therefore be apparent that the response to by TF-VIIa, further propagation of the clot occurs by feedback
vascular injury is a complex and precisely modulated process that amplification of thrombin through the intrinsic pathway factors