Page 620 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 620
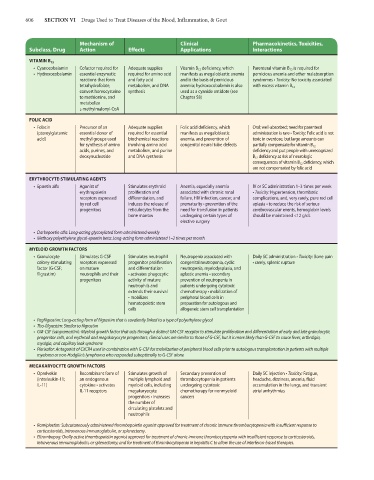
606 SECTION VI Drugs Used to Treat Diseases of the Blood, Inflammation, & Gout
Mechanism of Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Toxicities,
Subclass, Drug Action Effects Applications Interactions
VITAMIN B 12
• Cyanocobalamin Cofactor required for Adequate supplies Vitamin B 12 deficiency, which Parenteral vitamin B 12 is required for
• Hydroxocobalamin essential enzymatic required for amino acid manifests as megaloblastic anemia pernicious anemia and other malabsorption
reactions that form and fatty acid and is the basis of pernicious syndromes • Toxicity: No toxicity associated
tetrahydrofolate, metabolism, and DNA anemia; hydroxocobalamin is also with excess vitamin B 12
convert homocysteine synthesis used as a cyanide antidote (see
to methionine, and Chapter 58)
metabolize
l-methylmalonyl-CoA
FOLIC ACID
• Folacin Precursor of an Adequate supplies Folic acid deficiency, which Oral; well-absorbed; need for parenteral
(pteroylglutamic essential donor of required for essential manifests as megaloblastic administration is rare • Toxicity: Folic acid is not
acid) methyl groups used biochemical reactions anemia, and prevention of toxic in overdose, but large amounts can
for synthesis of amino involving amino acid congenital neural tube defects partially compensate for vitamin B 12
acids, purines, and metabolism, and purine deficiency and put people with unrecognized
deoxynucleotide and DNA synthesis B 12 deficiency at risk of neurologic
consequences of vitamin B 12 deficiency, which
are not compensated by folic acid
ERYTHROCYTE-STIMULATING AGENTS
• Epoetin alfa Agonist of Stimulates erythroid Anemia, especially anemia IV or SC administration 1–3 times per week
erythropoietin proliferation and associated with chronic renal • Toxicity: Hypertension, thrombotic
receptors expressed differentiation, and failure, HIV infection, cancer, and complications, and, very rarely, pure red cell
by red cell induces the release of prematurity • prevention of the aplasia • to reduce the risk of serious
progenitors reticulocytes from the need for transfusion in patients cerebrovascular events, hemoglobin levels
bone marrow undergoing certain types of should be maintained <12 g/dL
elective surgery
• Darbepoetin alfa: Long-acting glycosylated form administered weekly
• Methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta: Long-acting form administered 1–2 times per month
MYELOID GROWTH FACTORS
• Granulocyte Stimulates G-CSF Stimulates neutrophil Neutropenia associated with Daily SC administration • Toxicity: Bone pain
colony-stimulating receptors expressed progenitor proliferation congenital neutropenia, cyclic • rarely, splenic rupture
factor (G-CSF; on mature and differentiation neutropenia, myelodysplasia, and
filgrastim) neutrophils and their • activates phagocytic aplastic anemia • secondary
progenitors activity of mature prevention of neutropenia in
neutrophils and patients undergoing cytotoxic
extends their survival chemotherapy • mobilization of
• mobilizes peripheral blood cells in
hematopoietic stem preparation for autologous and
cells allogeneic stem cell transplantation
• Pegfilgrastim: Long-acting form of filgrastim that is covalently linked to a type of polyethylene glycol
• Tbo-filgrastim: Similar to filgrastim
• GM-CSF (sargramostim): Myeloid growth factor that acts through a distinct GM-CSF receptor to stimulate proliferation and differentiation of early and late granulocytic
progenitor cells, and erythroid and megakaryocyte progenitors; clinical uses are similar to those of G-CSF, but it is more likely than G-CSF to cause fever, arthralgia,
myalgia, and capillary leak syndrome
• Plerixafor: Antagonist of CXCR4 used in combination with G-CSF for mobilization of peripheral blood cells prior to autologous transplantation in patients with multiple
myeloma or non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma who responded suboptimally to G-CSF alone
MEGAKARYOCYTE GROWTH FACTORS
• Oprelvekin Recombinant form of Stimulates growth of Secondary prevention of Daily SC injection • Toxicity: Fatigue,
(interleukin-11; an endogenous multiple lymphoid and thrombocytopenia in patients headache, dizziness, anemia, fluid
IL-11) cytokine • activates myeloid cells, including undergoing cytotoxic accumulation in the lungs, and transient
IL-11 receptors megakaryocyte chemotherapy for nonmyeloid atrial arrhythmias
progenitors • increases cancers
the number of
circulating platelets and
neutrophils
• Romiplostim: Subcutaneously administered thrombopoietin agonist approved for treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenia with insufficient response to
corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, or splenectomy.
• Eltrombopag: Orally active thrombopoietin agonist approved for treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenia with insufficient response to corticosteroids,
intravenous immunoglobulin, or splenectomy; and for treatment of thrombocytopenia in hepatitis C to allow the use of interferon-based therapies.