Page 647 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 647
CHAPTER 35 Agents Used in Dyslipidemia 633
CH 3 CH 3
HO HO
COO – COO –
OH OH
S
CoA
HMG-CoA reduced Mevalonate
intermediate
HO O HO
COO –
O OH
O O
H 3 C O H 3 C O
CH 3 CH 3
CH 3 CH 3
H 3 C C
H 3
Lovastatin Lovastatin (active form)
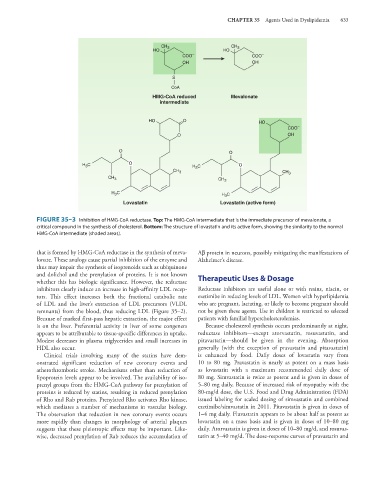
FIGURE 35–3 Inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Top: The HMG-CoA intermediate that is the immediate precursor of mevalonate, a
critical compound in the synthesis of cholesterol. Bottom: The structure of lovastatin and its active form, showing the similarity to the normal
HMG-CoA intermediate (shaded areas).
that is formed by HMG-CoA reductase in the synthesis of meva- Aβ protein in neurons, possibly mitigating the manifestations of
lonate. These analogs cause partial inhibition of the enzyme and Alzheimer’s disease.
thus may impair the synthesis of isoprenoids such as ubiquinone
and dolichol and the prenylation of proteins. It is not known Therapeutic Uses & Dosage
whether this has biologic significance. However, the reductase
inhibitors clearly induce an increase in high-affinity LDL recep- Reductase inhibitors are useful alone or with resins, niacin, or
tors. This effect increases both the fractional catabolic rate ezetimibe in reducing levels of LDL. Women with hyperlipidemia
of LDL and the liver’s extraction of LDL precursors (VLDL who are pregnant, lactating, or likely to become pregnant should
remnants) from the blood, thus reducing LDL (Figure 35–2). not be given these agents. Use in children is restricted to selected
Because of marked first-pass hepatic extraction, the major effect patients with familial hypercholesterolemias.
is on the liver. Preferential activity in liver of some congeners Because cholesterol synthesis occurs predominantly at night,
appears to be attributable to tissue-specific differences in uptake. reductase inhibitors—except atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, and
Modest decreases in plasma triglycerides and small increases in pitavastatin—should be given in the evening. Absorption
HDL also occur. generally (with the exception of pravastatin and pitavastatin)
Clinical trials involving many of the statins have dem- is enhanced by food. Daily doses of lovastatin vary from
onstrated significant reduction of new coronary events and 10 to 80 mg. Pravastatin is nearly as potent on a mass basis
atherothrombotic stroke. Mechanisms other than reduction of as lovastatin with a maximum recommended daily dose of
lipoprotein levels appear to be involved. The availability of iso- 80 mg. Simvastatin is twice as potent and is given in doses of
prenyl groups from the HMG-CoA pathway for prenylation of 5–80 mg daily. Because of increased risk of myopathy with the
proteins is reduced by statins, resulting in reduced prenylation 80-mg/d dose, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
of Rho and Rab proteins. Prenylated Rho activates Rho kinase, issued labeling for scaled dosing of simvastatin and combined
which mediates a number of mechanisms in vascular biology. ezetimibe/simvastatin in 2011. Pitavastatin is given in doses of
The observation that reduction in new coronary events occurs 1–4 mg daily. Fluvastatin appears to be about half as potent as
more rapidly than changes in morphology of arterial plaques lovastatin on a mass basis and is given in doses of 10–80 mg
suggests that these pleiotropic effects may be important. Like- daily. Atorvastatin is given in doses of 10–80 mg/d, and rosuvas-
wise, decreased prenylation of Rab reduces the accumulation of tatin at 5–40 mg/d. The dose-response curves of pravastatin and