Page 643 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 643
CHAPTER 35 Agents Used in Dyslipidemia 629
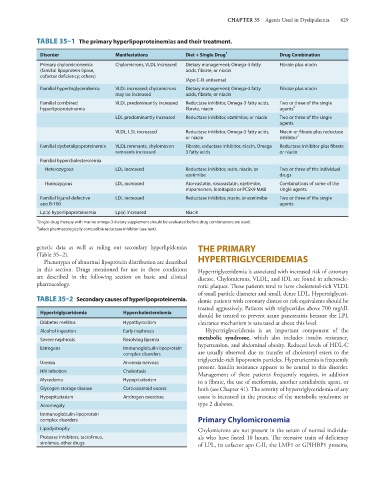
TABLE 35–1 The primary hyperlipoproteinemias and their treatment.
Disorder Manifestations Diet + Single Drug 1 Drug Combination
Primary chylomicronemia Chylomicrons, VLDL increased Dietary management; Omega-3 fatty Fibrate plus niacin
(familial lipoprotein lipase, acids, fibrate, or niacin
cofactor deficiency; others)
(Apo C-III antisense)
Familial hypertriglyceridemia VLDL increased; chylomicrons Dietary management; Omega-3 fatty Fibrate plus niacin
may be increased acids, fibrate, or niacin
Familial combined VLDL predominantly increased Reductase inhibitor, Omega-3 fatty acids, Two or three of the single
hyperlipoproteinemia fibrate, niacin agents 2
LDL predominantly increased Reductase inhibitor, ezetimibe, or niacin Two or three of the single
agents
VLDL, LDL increased Reductase inhibitor, Omega-3 fatty acids, Niacin or fibrate plus reductase
or niacin inhibitor 2
Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia VLDL remnants, chylomicron Fibrate, reductase inhibitor, niacin, Omega Reductase inhibitor plus fibrate
remnants increased 3 fatty acids or niacin
Familial hypercholesterolemia
Heterozygous LDL increased Reductase inhibitor, resin, niacin, or Two or three of the individual
ezetimibe drugs
Homozygous LDL increased Atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, ezetimibe, Combinations of some of the
mipomersen, lomitapide or PCSK9 MAB single agents
Familial ligand-defective LDL increased Reductase inhibitor, niacin, or ezetimibe Two or three of the single
apo B-100 agents
Lp(a) hyperlipoproteinemia Lp(a) increased Niacin
1 Single-drug therapy with marine omega-3 dietary supplement should be evaluated before drug combinations are used.
2
Select pharmacologically compatible reductase inhibitor (see text).
genetic data as well as ruling out secondary hyperlipidemias THE PRIMARY
(Table 35–2).
Phenotypes of abnormal lipoprotein distribution are described HYPERTRIGLYCERIDEMIAS
in this section. Drugs mentioned for use in these conditions Hypertriglyceridemia is associated with increased risk of coronary
are described in the following section on basic and clinical disease. Chylomicrons, VLDL, and IDL are found in atheroscle-
pharmacology. rotic plaques. These patients tend to have cholesterol-rich VLDL
of small particle diameter and small, dense LDL. Hypertriglyceri-
TABLE 35–2 Secondary causes of hyperlipoproteinemia. demic patients with coronary disease or risk equivalents should be
treated aggressively. Patients with triglycerides above 700 mg/dL
Hypertriglyceridemia Hypercholesterolemia
should be treated to prevent acute pancreatitis because the LPL
Diabetes mellitus Hypothyroidism clearance mechanism is saturated at about this level.
Alcohol ingestion Early nephrosis Hypertriglyceridemia is an important component of the
Severe nephrosis Resolving lipemia metabolic syndrome, which also includes insulin resistance,
hypertension, and abdominal obesity. Reduced levels of HDL-C
Estrogens Immunoglobulin-lipoprotein
complex disorders are usually observed due to transfer of cholesteryl esters to the
triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particles. Hyperuricemia is frequently
Uremia Anorexia nervosa
present. Insulin resistance appears to be central to this disorder.
HIV infection Cholestasis
Management of these patients frequently requires, in addition
Myxedema Hypopituitarism to a fibrate, the use of metformin, another antidiabetic agent, or
Glycogen storage disease Corticosteroid excess both (see Chapter 41). The severity of hypertriglyceridemia of any
Hypopituitarism Androgen overdose cause is increased in the presence of the metabolic syndrome or
Acromegaly type 2 diabetes.
Immunoglobulin-lipoprotein
complex disorders Primary Chylomicronemia
Lipodystrophy Chylomicrons are not present in the serum of normal individu-
Protease inhibitors, tacrolimus, als who have fasted 10 hours. The recessive traits of deficiency
sirolimus, other drugs of LPL, its cofactor apo C-II, the LMF1 or GPIHBP1 proteins,