Page 932 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 932
918 SECTION VIII Chemotherapeutic Drugs
may be appropriate for travelers to carry supplies of drugs with
them in case they develop a febrile illness when medical atten-
tion is unavailable. Regimens for self-treatment include new
artemisinin-based combination therapies (see below), which are
†
widely available internationally (and, in the case of Coartem , in
the USA); Malarone; mefloquine; and quinine. Most authorities
Blood do not recommend routine terminal chemoprophylaxis with pri-
schizonticide Gametocide maquine to eradicate dormant hepatic stages of P vivax and P ovale
after travel, but this may be appropriate in some circumstances,
especially for travelers with major exposure to these parasites.
Blood
Multiple drugs are available for the treatment of malaria that
Liver presents in the USA (Table 52–3). Most nonfalciparum infections
and falciparum malaria from areas without known resistance should
Schizonts
be treated with chloroquine. For vivax malaria from areas with sus-
pected chloroquine resistance, including Indonesia and Papua New
Guinea, other therapies effective against falciparum malaria may be
Tissue used. Vivax and ovale malaria should subsequently be treated with
schizonticide
primaquine to eradicate liver forms. Uncomplicated falciparum
malaria from most areas is most often treated with Malarone, but new
artemisinin-based combinations are increasingly the international
Hypnozoites
standard of care, and one combination, Coartem, is now available in
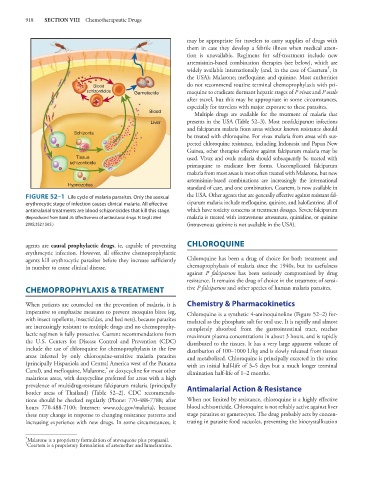
FIGURE 52–1 Life cycle of malaria parasites. Only the asexual the USA. Other agents that are generally effective against resistant fal-
erythrocytic stage of infection causes clinical malaria. All effective ciparum malaria include mefloquine, quinine, and halofantrine, all of
antimalarial treatments are blood schizonticides that kill this stage. which have toxicity concerns at treatment dosages. Severe falciparum
(Reproduced from Baird JK: Effectiveness of antimalarial drugs. N Engl J Med malaria is treated with intravenous artesunate, quinidine, or quinine
2005;352:1565.) (intravenous quinine is not available in the USA).
agents are causal prophylactic drugs, ie, capable of preventing CHLOROQUINE
erythrocytic infection. However, all effective chemoprophylactic
agents kill erythrocytic parasites before they increase sufficiently Chloroquine has been a drug of choice for both treatment and
in number to cause clinical disease. chemoprophylaxis of malaria since the 1940s, but its usefulness
against P falciparum has been seriously compromised by drug
resistance. It remains the drug of choice in the treatment of sensi-
CHEMOPROPHYLAXIS & TREATMENT tive P falciparum and other species of human malaria parasites.
When patients are counseled on the prevention of malaria, it is Chemistry & Pharmacokinetics
imperative to emphasize measures to prevent mosquito bites (eg, Chloroquine is a synthetic 4-aminoquinoline (Figure 52–2) for-
with insect repellents, insecticides, and bed nets), because parasites mulated as the phosphate salt for oral use. It is rapidly and almost
are increasingly resistant to multiple drugs and no chemoprophy- completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, reaches
lactic regimen is fully protective. Current recommendations from maximum plasma concentrations in about 3 hours, and is rapidly
the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) distributed to the tissues. It has a very large apparent volume of
include the use of chloroquine for chemoprophylaxis in the few distribution of 100–1000 L/kg and is slowly released from tissues
areas infested by only chloroquine-sensitive malaria parasites and metabolized. Chloroquine is principally excreted in the urine
(principally Hispaniola and Central America west of the Panama with an initial half-life of 3–5 days but a much longer terminal
*
Canal), and mefloquine, Malarone, or doxycycline for most other elimination half-life of 1–2 months.
malarious areas, with doxycycline preferred for areas with a high
prevalence of multidrug-resistant falciparum malaria (principally Antimalarial Action & Resistance
border areas of Thailand) (Table 52–2). CDC recommenda-
tions should be checked regularly (Phone: 770-488-7788; after When not limited by resistance, chloroquine is a highly effective
hours 770-488-7100; Internet: www.cdc.gov/malaria), because blood schizonticide. Chloroquine is not reliably active against liver
these may change in response to changing resistance patterns and stage parasites or gametocytes. The drug probably acts by concen-
increasing experience with new drugs. In some circumstances, it trating in parasite food vacuoles, preventing the biocrystallization
* Malarone is a proprietary formulation of atovaquone plus proguanil.
† Coartem is a proprietary formulation of artemether and lumefantrine.