Page 935 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 935
CHAPTER 52 Antiprotozoal Drugs 921
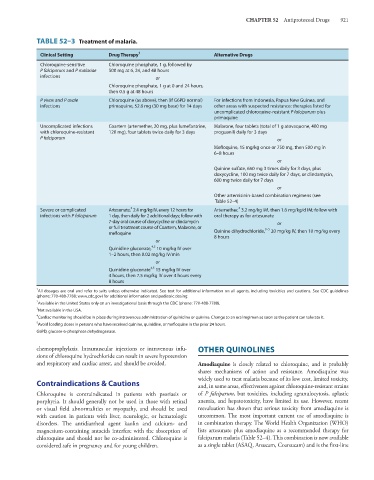
TABLE 52–3 Treatment of malaria.
Clinical Setting Drug Therapy 1 Alternative Drugs
Chloroquine-sensitive Chloroquine phosphate, 1 g, followed by
P falciparum and P malariae 500 mg at 6, 24, and 48 hours
infections or
Chloroquine phosphate, 1 g at 0 and 24 hours,
then 0.5 g at 48 hours
P vivax and P ovale Chloroquine (as above), then (if G6PD normal) For infections from Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and
infections primaquine, 52.6 mg (30 mg base) for 14 days other areas with suspected resistance: therapies listed for
uncomplicated chloroquine-resistant P falciparum plus
primaquine
Uncomplicated infections Coartem (artemether, 20 mg, plus lumefantrine, Malarone, four tablets (total of 1 g atovaquone, 400 mg
with chloroquine-resistant 120 mg), four tablets twice daily for 3 days proguanil) daily for 3 days
P falciparum or
Mefloquine, 15 mg/kg once or 750 mg, then 500 mg in
6–8 hours
or
Quinine sulfate, 650 mg 3 times daily for 3 days, plus
doxycycline, 100 mg twice daily for 7 days, or clindamycin,
600 mg twice daily for 7 days
or
Other artemisinin-based combination regimens (see
Table 52–4)
2
3
Severe or complicated Artesunate, 2.4 mg/kg IV, every 12 hours for Artemether, 3.2 mg/kg IM, then 1.6 mg/kg/d IM; follow with
infections with P falciparum 1 day, then daily for 2 additional days; follow with oral therapy as for artesunate
7-day oral course of doxycycline or clindamycin or
or full treatment course of Coartem, Malarone, or 3–5
mefloquine Quinine dihydrochloride, 20 mg/kg IV, then 10 mg/kg every
8 hours
or
4,5
Quinidine gluconate, 10 mg/kg IV over
1–2 hours, then 0.02 mg/kg IV/min
or
4,5
Quinidine gluconate 15 mg/kg IV over
4 hours, then 7.5 mg/kg IV over 4 hours every
8 hours
1
All dosages are oral and refer to salts unless otherwise indicated. See text for additional information on all agents, including toxicities and cautions. See CDC guidelines
(phone: 770-488-7788; www.cdc.gov) for additional information and pediatric dosing.
2
Available in the United States only on an investigational basis through the CDC (phone: 770-488-7788).
3 Not available in the USA.
4
Cardiac monitoring should be in place during intravenous administration of quinidine or quinine. Change to an oral regimen as soon as the patient can tolerate it.
5 Avoid loading doses in persons who have received quinine, quinidine, or mefloquine in the prior 24 hours.
G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
chemoprophylaxis. Intramuscular injections or intravenous infu- OTHER QUINOLINES
sions of chloroquine hydrochloride can result in severe hypotension
and respiratory and cardiac arrest, and should be avoided. Amodiaquine is closely related to chloroquine, and it probably
shares mechanisms of action and resistance. Amodiaquine was
widely used to treat malaria because of its low cost, limited toxicity,
Contraindications & Cautions and, in some areas, effectiveness against chloroquine-resistant strains
Chloroquine is contraindicated in patients with psoriasis or of P falciparum, but toxicities, including agranulocytosis, aplastic
porphyria. It should generally not be used in those with retinal anemia, and hepatotoxicity, have limited its use. However, recent
or visual field abnormalities or myopathy, and should be used reevaluation has shown that serious toxicity from amodiaquine is
with caution in patients with liver, neurologic, or hematologic uncommon. The most important current use of amodiaquine is
disorders. The antidiarrheal agent kaolin and calcium- and in combination therapy. The World Health Organization (WHO)
magnesium-containing antacids interfere with the absorption of lists artesunate plus amodiaquine as a recommended therapy for
chloroquine and should not be co-administered. Chloroquine is falciparum malaria (Table 52–4). This combination is now available
considered safe in pregnancy and for young children. as a single tablet (ASAQ, Arsucam, Coarsucam) and is the first-line