Page 934 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 934
920 SECTION VIII Chemotherapeutic Drugs
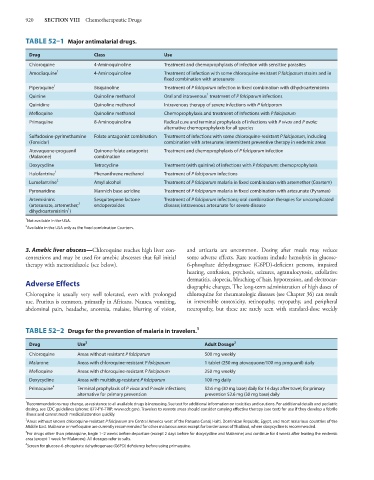
TABLE 52–1 Major antimalarial drugs.
Drug Class Use
Chloroquine 4-Aminoquinoline Treatment and chemoprophylaxis of infection with sensitive parasites
Amodiaquine 1 4-Aminoquinoline Treatment of infection with some chloroquine-resistant P falciparum strains and in
fixed combination with artesunate
Piperaquine 1 Bisquinoline Treatment of P falciparum infection in fixed combination with dihydroartemisinin
1
Quinine Quinoline methanol Oral and intravenous treatment of P falciparum infections
Quinidine Quinoline methanol Intravenous therapy of severe infections with P falciparum
Mefloquine Quinoline methanol Chemoprophylaxis and treatment of infections with P falciparum
Primaquine 8-Aminoquinoline Radical cure and terminal prophylaxis of infections with P vivax and P ovale;
alternative chemoprophylaxis for all species
Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine Folate antagonist combination Treatment of infections with some chloroquine-resistant P falciparum, including
(Fansidar) combination with artesunate; intermittent preventive therapy in endemic areas
Atovaquone-proguanil Quinone-folate antagonist Treatment and chemoprophylaxis of P falciparum infection
(Malarone) combination
Doxycycline Tetracycline Treatment (with quinine) of infections with P falciparum; chemoprophylaxis
Halofantrine 1 Phenanthrene methanol Treatment of P falciparum infections
Lumefantrine 2 Amyl alcohol Treatment of P falciparum malaria in fixed combination with artemether (Coartem)
Pyronaridine Mannich base acridine Treatment of P falciparum malaria in fixed combination with artesunate (Pyramax)
Artemisinins Sesquiterpene lactone Treatment of P falciparum infections; oral combination therapies for uncomplicated
2
(artesunate, artemether, endoperoxides disease; intravenous artesunate for severe disease
1
dihydroartemisinin )
1 Not available in the USA.
2
Available in the USA only as the fixed combination Coartem.
3. Amebic liver abscess—Chloroquine reaches high liver con- and urticaria are uncommon. Dosing after meals may reduce
centrations and may be used for amebic abscesses that fail initial some adverse effects. Rare reactions include hemolysis in glucose-
therapy with metronidazole (see below). 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)-deficient persons, impaired
hearing, confusion, psychosis, seizures, agranulocytosis, exfoliative
Adverse Effects dermatitis, alopecia, bleaching of hair, hypotension, and electrocar-
diographic changes. The long-term administration of high doses of
Chloroquine is usually very well tolerated, even with prolonged chloroquine for rheumatologic diseases (see Chapter 36) can result
use. Pruritus is common, primarily in Africans. Nausea, vomiting, in irreversible ototoxicity, retinopathy, myopathy, and peripheral
abdominal pain, headache, anorexia, malaise, blurring of vision, neuropathy, but these are rarely seen with standard-dose weekly
TABLE 52–2 Drugs for the prevention of malaria in travelers. 1
Drug Use 2 Adult Dosage 3
Chloroquine Areas without resistant P falciparum 500 mg weekly
Malarone Areas with chloroquine-resistant P falciparum 1 tablet (250 mg atovaquone/100 mg proguanil) daily
Mefloquine Areas with chloroquine-resistant P falciparum 250 mg weekly
Doxycycline Areas with multidrug-resistant P falciparum 100 mg daily
Primaquine 4 Terminal prophylaxis of P vivax and P ovale infections; 52.6 mg (30 mg base) daily for 14 days after travel; for primary
alternative for primary prevention prevention 52.6 mg (30 mg base) daily
1 Recommendations may change, as resistance to all available drugs is increasing. See text for additional information on toxicities and cautions. For additional details and pediatric
dosing, see CDC guidelines (phone: 877-FYI-TRIP; www.cdc.gov). Travelers to remote areas should consider carrying effective therapy (see text) for use if they develop a febrile
illness and cannot reach medical attention quickly.
2
Areas without known chloroquine-resistant P falciparum are Central America west of the Panama Canal, Haiti, Dominican Republic, Egypt, and most malarious countries of the
Middle East. Malarone or mefloquine are currently recommended for other malarious areas except for border areas of Thailand, where doxycycline is recommended.
3
For drugs other than primaquine, begin 1–2 weeks before departure (except 2 days before for doxycycline and Malarone) and continue for 4 weeks after leaving the endemic
area (except 1 week for Malarone). All dosages refer to salts.
4
Screen for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency before using primaquine.