Page 967 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 967
CHAPTER 54 Cancer Chemotherapy 953
the anthracyclines, vinca alkaloids, taxanes, camptothecins, Mechanism of Action
epipodophyllotoxins, and even small molecule inhibitors, such
as imatinib. As a class, the alkylating agents exert their cytotoxic effects via
transfer of their alkyl groups to various cellular constituents.
Alkylation of DNA within the nucleus probably represents the
■ BASIC PHARMACOLOGY OF major interaction leading to cell death. However, these drugs
react chemically with sulfhydryl, amino, hydroxyl, carboxyl, and
CANCER CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC phosphate groups of other cellular nucleophiles as well. The gen-
DRUGS eral mechanism of action of these drugs involves intramolecular
cyclization to form an ethyleneimonium ion that may directly
ALKYLATING AGENTS or through formation of a carbonium ion transfer an alkyl group
to a cellular constituent. In addition to alkylation, a secondary
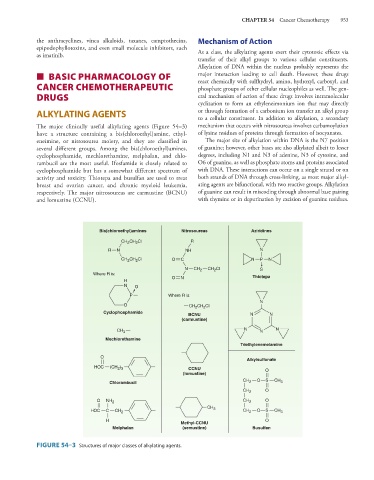
The major clinically useful alkylating agents (Figure 54–3) mechanism that occurs with nitrosoureas involves carbamoylation
have a structure containing a bis(chloroethyl)amine, ethyl- of lysine residues of proteins through formation of isocyanates.
eneimine, or nitrosourea moiety, and they are classified in The major site of alkylation within DNA is the N7 position
several different groups. Among the bis(chloroethyl)amines, of guanine; however, other bases are also alkylated albeit to lesser
cyclophosphamide, mechlorethamine, melphalan, and chlo- degrees, including N1 and N3 of adenine, N3 of cytosine, and
rambucil are the most useful. Ifosfamide is closely related to O6 of guanine, as well as phosphate atoms and proteins associated
cyclophosphamide but has a somewhat different spectrum of with DNA. These interactions can occur on a single strand or on
activity and toxicity. Thiotepa and busulfan are used to treat both strands of DNA through cross-linking, as most major alkyl-
breast and ovarian cancer, and chronic myeloid leukemia, ating agents are bifunctional, with two reactive groups. Alkylation
respectively. The major nitrosoureas are carmustine (BCNU) of guanine can result in miscoding through abnormal base pairing
and lomustine (CCNU). with thymine or in depurination by excision of guanine residues.
Bis(chloroethyl)amines Nitrosoureas Aziridines
CH CH CI R
2
2
R N NH N
CH 2 CH 2 CI O C N P N
N CH 2 CH CI S
2
Where R is:
O N Thiotepa
H
N O
P Where R is:
N
O CH CH 2 CI
2
Cyclophosphamide BCNU N N
(carmustine)
CH 3 N N N
Mechlorethamine
Triethylenemelamine
O
Alkylsulfonate
HOC (CH ) 3 CCNU O
2
(lomustine)
Chlorambucil CH 2 O S CH 3
CH 2 O
O NH 2 CH 2 O
CH 3
HOC C CH 2 CH 2 O S CH 3
H O
Methyl-CCNU
Melphalan (semustine) Busulfan
FIGURE 54–3 Structures of major classes of alkylating agents.