Page 964 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 964
950 SECTION VIII Chemotherapeutic Drugs
is most often administered in the treatment of anal cancer, bladder Death
cancer, breast cancer, gastroesophageal cancer, laryngeal cancer, 10 12
locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), osteogenic
sarcoma, and locally advanced rectal cancer. For diseases such as Symptoms
anal cancer, gastroesophageal cancer, laryngeal cancer, NSCLC, 10 10
and rectal cancer, optimal clinical benefit is derived when chemo- Diagnosis
therapy is administered with radiation therapy either concurrently
or sequentially. The goal of the neoadjuvant approach is to reduce 10 8
the size of the primary tumor so that surgical resection can be Subclinical
made easier and more effective. In addition, with rectal cancer and
laryngeal cancer, the administration of combined modality ther- Number of cancer cells (log scale) 10 6
apy prior to surgery can result in sparing of vital normal organs,
such as the rectum or larynx. In general, additional chemotherapy
is given for a defined period of time, usually 3–4 months, after 10 4 Surgery
surgery has been performed.
One of the most important roles for cancer chemotherapy is as
an adjuvant to local treatment modalities such as surgery, and this 10 2
has been termed adjuvant chemotherapy. In this setting, chemo-
therapy is administered after surgery has been performed, and the
goal of chemotherapy is to reduce the incidence of both local and 10 0
systemic recurrence and to improve the overall survival of patients. Time
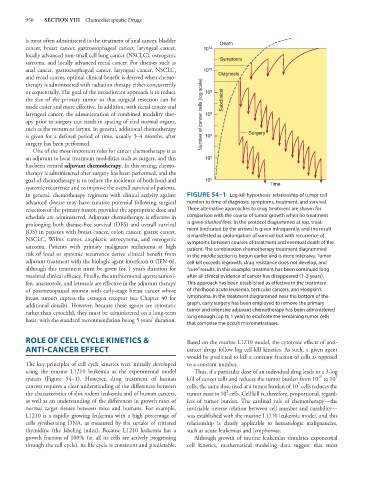
In general, chemotherapy regimens with clinical activity against FIGURE 54–1 Log-kill hypothesis: relationship of tumor cell
advanced disease may have curative potential following surgical number to time of diagnosis, symptoms, treatment, and survival.
resection of the primary tumor, provided the appropriate dose and Three alternative approaches to drug treatment are shown for
schedule are administered. Adjuvant chemotherapy is effective in comparison with the course of tumor growth when no treatment
prolonging both disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival is given (dashed line). In the protocol diagrammed at top, treat-
(OS) in patients with breast cancer, colon cancer, gastric cancer, ment (indicated by the arrows) is given infrequently, and the result
NSCLC, Wilms’ tumor, anaplastic astrocytoma, and osteogenic is manifested as prolongation of survival but with recurrence of
symptoms between courses of treatment and eventual death of the
sarcoma. Patients with primary malignant melanoma at high patient. The combination chemotherapy treatment diagrammed
risk of local or systemic recurrence derive clinical benefit from in the middle section is begun earlier and is more intensive. Tumor
adjuvant treatment with the biologic agent interferon α (IFN-α), cell kill exceeds regrowth, drug resistance does not develop, and
although this treatment must be given for 1 year’s duration for “cure” results. In this example, treatment has been continued long
maximal clinical efficacy. Finally, the antihormonal agents tamoxi- after all clinical evidence of cancer has disappeared (1–3 years).
fen, anastrozole, and letrozole are effective in the adjuvant therapy This approach has been established as effective in the treatment
of postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer whose of childhood acute leukemia, testicular cancers, and Hodgkin’s
breast tumors express the estrogen receptor (see Chapter 40 for lymphoma. In the treatment diagrammed near the bottom of the
additional details). However, because these agents are cytostatic graph, early surgery has been employed to remove the primary
rather than cytocidal, they must be administered on a long-term tumor and intensive adjuvant chemotherapy has been administered
basis, with the standard recommendation being 5 years’ duration. long enough (up to 1 year) to eradicate the remaining tumor cells
that comprise the occult micrometastases.
ROLE OF CELL CYCLE KINETICS & Based on the murine L1210 model, the cytotoxic effects of anti-
ANTI-CANCER EFFECT cancer drugs follow log cell-kill kinetics. As such, a given agent
would be predicted to kill a constant fraction of cells as opposed
The key principles of cell cycle kinetics were initially developed to a constant number.
using the murine L1210 leukemia as the experimental model Thus, if a particular dose of an individual drug leads to a 3-log
10
7
system (Figure 54–1). However, drug treatment of human kill of cancer cells and reduces the tumor burden from 10 to 10
5
cancers requires a clear understanding of the differences between cells, the same dose used at a tumor burden of 10 cells reduces the
2
the characteristics of this rodent leukemia and of human cancers, tumor mass to 10 cells. Cell kill is, therefore, proportional, regard-
as well as an understanding of the differences in growth rates of less of tumor burden. The cardinal rule of chemotherapy—the
normal target tissues between mice and humans. For example, invariable inverse relation between cell number and curability—
L1210 is a rapidly growing leukemia with a high percentage of was established with the murine L1210 leukemia model, and this
cells synthesizing DNA, as measured by the uptake of tritiated relationship is clearly applicable to hematologic malignancies,
thymidine (the labeling index). Because L1210 leukemia has a such as acute leukemias and lymphomas.
growth fraction of 100% (ie, all its cells are actively progressing Although growth of murine leukemias simulates exponential
through the cell cycle), its life cycle is consistent and predictable. cell kinetics, mathematical modeling data suggest that most