Page 965 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 965
CHAPTER 54 Cancer Chemotherapy 951
human solid tumors do not grow in such an exponential manner. TABLE 54–1 Cell cycle effects of major classes of
Rather, the experimental data in human solid cancers support a anti-cancer drugs.
Gompertzian model of tumor growth and regression. The critical
distinction between Gompertzian and exponential growth is Cell Cycle-Specific Cell Cycle-Nonspecific
that the growth fraction of the tumor is not constant with (CCS) Agents (CCNS) Agents
Gompertzian kinetics but instead decreases exponentially Antimetabolites (S phase) Alkylating agents
with time (exponential growth is matched by exponential retarda- Capecitabine Altretamine
tion of growth, due to blood supply limitations and other factors). Cladribine Bendamustine
The growth fraction peaks when the tumor is approximately one-
third its maximum size. According to the Gompertzian model, Clofarabine Busulfan
when a patient with advanced cancer is treated, the tumor mass Cytarabine (ara-C) Carmustine
is larger, its growth fraction is low, and the fraction of cells Fludarabine Chlorambucil
killed is, therefore, small. An important feature of Gompertzian 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Cyclophosphamide
growth is that response to chemotherapy in drug-sensitive tumors Gemcitabine Dacarbazine
depends, in large measure, on where the tumor is in its particular 6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP) Lomustine
growth curve.
Information on cell and population kinetics of cancer cells Methotrexate (MTX) Mechlorethamine
explains, in part, the limited effectiveness of most available Nelarabine Melphalan
anticancer drugs. A schematic summary of cell cycle kinetics Pralatrexate Temozolomide
is presented in Figure 54–2. This information is relevant to 6-Thioguanine (6-TG) Thiotepa
the mode of action, indications, and scheduling of cell cycle– Topoisomerase II inhibitor Antitumor antibiotics
specific (CCS) and cell cycle–nonspecific (CCNS) drugs. (G 1 –S phase) Dactinomycin
Agents falling into these two major classes are summarized
in Table 54–1. Etoposide Mitomycin
Topoisomerase I inhibitors Platinum analogs
The Role of Drug Combinations (Camptothecins, G 2 -M) Carboplatin
Irinotecan Cisplatin
With rare exceptions (eg, choriocarcinoma and Burkitt’s lym-
phoma), single drugs are unable to cure cancers when they Topotecan Oxaliplatin
are in an advanced stage. In the 1960s and early 1970s, drug Taxanes (M phase) Anthracyclines
Albumin-bound paclitaxel Daunorubicin
Cabazitaxel Doxorubicin
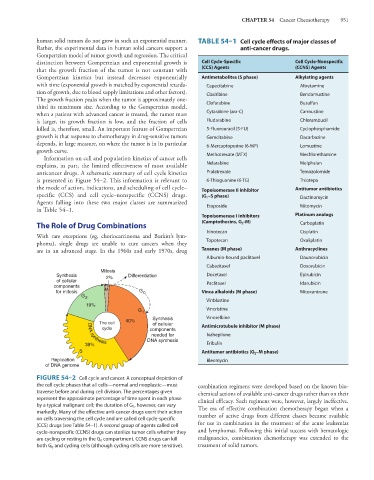
Mitosis
Synthesis 2% Differentiation Docetaxel Epirubicin
of cellular Paclitaxel Idarubicin
components
for mitosis M G 0 Vinca alkaloids (M phase) Mitoxantrone
G 2
Vinblastine
19%
G 1 Vincristine
Synthesis Vinorelbine
The cell 40% of cellular
cycle components Antimicrotubule inhibitor (M phase)
needed for Ixabepilone
DNA synthesis
DNA synthesis
39% Eribulin
S Antitumor antibiotics (G 2 –M phase)
Replication Bleomycin
of DNA genome
FIGURE 54–2 Cell cycle and cancer. A conceptual depiction of
the cell cycle phases that all cells—normal and neoplastic—must combination regimens were developed based on the known bio-
traverse before and during cell division. The percentages given chemical actions of available anti-cancer drugs rather than on their
represent the approximate percentage of time spent in each phase clinical efficacy. Such regimens were, however, largely ineffective.
by a typical malignant cell; the duration of G 1 , however, can vary The era of effective combination chemotherapy began when a
markedly. Many of the effective anti-cancer drugs exert their action
on cells traversing the cell cycle and are called cell cycle-specific number of active drugs from different classes became available
(CCS) drugs (see Table 54–1). A second group of agents called cell for use in combination in the treatment of the acute leukemias
cycle-nonspecific (CCNS) drugs can sterilize tumor cells whether they and lymphomas. Following this initial success with hematologic
are cycling or resting in the G 0 compartment. CCNS drugs can kill malignancies, combination chemotherapy was extended to the
both G 0 and cycling cells (although cycling cells are more sensitive). treatment of solid tumors.