Page 975 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 975
CHAPTER 54 Cancer Chemotherapy 961
6-methylmercaptopurine ribotide (MMPR) also are formed from triphosphate interferes with the processes of DNA synthesis
6-MP. These metabolites may contribute to its cytotoxic action. and DNA repair through inhibition of DNA polymerase-α
6-Thioguanine (6-TG) also inhibits several enzymes in the de and DNA polymerase-β. The triphosphate form can also be
novo purine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway. Various metabolic directly incorporated into DNA, resulting in inhibition of DNA
lesions result, including inhibition of purine nucleotide intercon- synthesis and function. The diphosphate metabolite of fludara-
version; decrease in intracellular levels of guanine nucleotides, bine inhibits ribonucleotide reductase, leading to inhibition of
which leads to inhibition of glycoprotein synthesis; interference essential deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates. Finally, fludarabine
with the formation of DNA and RNA; and incorporation of induces apoptosis in susceptible cells through as yet unde-
thiopurine nucleotides into both DNA and RNA. 6-TG has a termined mechanisms. This purine nucleotide analog is used
synergistic action when used together with cytarabine in the treat- mainly in the treatment of low-grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
ment of adult acute leukemia. and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). It is given parenter-
6-MP is converted to an inactive metabolite (6-thiouric ally, and up to 25–30% of parent drug is excreted in the urine.
acid) by an oxidation reaction catalyzed by xanthine oxidase, The main dose-limiting toxicity is myelosuppression. This agent
whereas 6-TG undergoes deamination. This is an important is a potent immunosuppressant with inhibitory effects on CD4
difference because the purine analog allopurinol, a potent xanthine and CD8 T cells. Patients are at increased risk for opportunistic
oxidase inhibitor, is frequently used as a supportive care measure infections, including fungi, herpes, and Pneumocystis jiroveci
in the treatment of acute leukemias to prevent the development pneumonia (PCP). Patients should receive PCP prophylaxis with
of hyperuricemia that often occurs with tumor cell lysis. Because trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (double strength) at least three
allopurinol inhibits xanthine oxidase, simultaneous therapy with times a week, and this should continue for up to 1 year after
allopurinol and 6-MP would result in increased levels of 6-MP, stopping fludarabine therapy.
thereby leading to excessive toxicity. In this setting, the dose of
mercaptopurine must be reduced by 50–75%. In contrast, such Cladribine
an interaction does not occur with 6-TG, which can be used in
full doses with allopurinol. Cladribine (2-chlorodeoxyadenosine) is a purine nucleoside ana-
log with high specificity for lymphoid cells. Inactive in its parent
form, it is initially phosphorylated by deoxycytidine kinase to
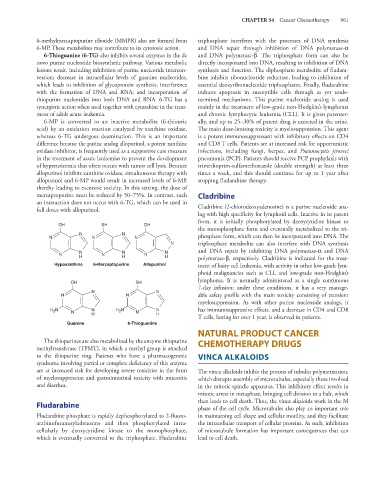
OH SH OH
the monophosphate form and eventually metabolized to the tri-
N N phosphate form, which can then be incorporated into DNA. The
N N N
N triphosphate metabolite can also interfere with DNA synthesis
N N N and DNA repair by inhibiting DNA polymerase-α and DNA
N N N
H H H polymerase-β, respectively. Cladribine is indicated for the treat-
Hypoxanthine 6-Mercaptopurine Allopurinol ment of hairy cell leukemia, with activity in other low-grade lym-
phoid malignancies such as CLL and low-grade non-Hodgkin’s
lymphoma. It is normally administered as a single continuous
OH SH
7-day infusion; under these conditions, it has a very manage-
N N
N N able safety profile with the main toxicity consisting of transient
myelosuppression. As with other purine nucleoside analogs, it
H N N N H N N N has immunosuppressive effects, and a decrease in CD4 and CD8
2
2
H H
T cells, lasting for over 1 year, is observed in patients.
Guanine 6-Thioguanine
NATURAL PRODUCT CANCER
The thiopurines are also metabolized by the enzyme thiopurine CHEMOTHERAPY DRUGS
methyltransferase (TPMT), in which a methyl group is attached
to the thiopurine ring. Patients who have a pharmacogenetic VINCA ALKALOIDS
syndrome involving partial or complete deficiency of this enzyme
are at increased risk for developing severe toxicities in the form The vinca alkaloids inhibit the process of tubulin polymerization,
of myelosuppression and gastrointestinal toxicity with mucositis which disrupts assembly of microtubules, especially those involved
and diarrhea. in the mitotic spindle apparatus. This inhibitory effect results in
mitotic arrest in metaphase, bringing cell division to a halt, which
Fludarabine then leads to cell death. Thus, the vinca alkaloids work in the M
phase of the cell cycle. Microtubules also play an important role
Fludarabine phosphate is rapidly dephosphorylated to 2-fluoro- in maintaining cell shape and cellular motility, and they facilitate
arabinofuranosyladenosine and then phosphorylated intra- the intracellular transport of cellular proteins. As such, inhibition
cellularly by deoxycytidine kinase to the monophosphate, of microtubule formation has important consequences that can
which is eventually converted to the triphosphate. Fludarabine lead to cell death.