Page 977 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 977
CHAPTER 54 Cancer Chemotherapy 963
Vincristine microtubules with enhancement of tubulin polymerization. This
promotion of microtubule assembly by paclitaxel results in inhibi-
Vincristine is another alkaloid derivative of Vinca rosea and is tion of mitosis and cell division. As such, paclitaxel and the other
closely related in structure to vinblastine. Its mechanism of action, taxanes work in the M phase of the cell cycle.
mechanism of resistance, and clinical pharmacology are identical Paclitaxel has significant activity in a broad range of solid
to those of vinblastine. Despite these similarities to vinblastine, tumors, including ovarian, advanced breast, NSCLC and small
vincristine has a strikingly different spectrum of clinical activity cell lung cancer (SCLC), head and neck, esophageal, prostate,
and safety profile, which results, in large part, from its higher and bladder cancers, as well as AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma. It
affinity for axonal microtubules.
is metabolized extensively by the liver P450 system, and nearly
80% of the drug is excreted in feces via the hepatobiliary route.
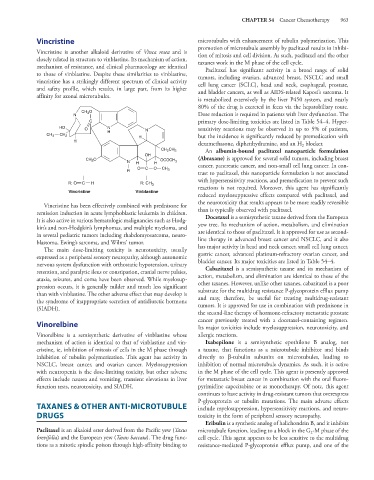
CH 3 O
N Dose reduction is required in patients with liver dysfunction. The
C primary dose-limiting toxicities are listed in Table 54–4. Hyper-
HO O N sensitivity reactions may be observed in up to 5% of patients,
H N
CH 3 CH 2 H but the incidence is significantly reduced by premedication with
H
dexamethasone, diphenhydramine, and an H blocker.
2
CH 2 CH 3 An albumin-bound paclitaxel nanoparticle formulation
OH
CH 3 O (Abraxane) is approved for several solid tumors, including breast
N H H OCOCH 3 cancer, pancreatic cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer. In con-
O C O CH 3
R trast to paclitaxel, this nanoparticle formulation is not associated
with hypersensitivity reactions, and premedication to prevent such
R: O C H R: CH 3 reactions is not required. Moreover, this agent has significantly
Vincristine Vinblastine
reduced myelosuppressive effects compared with paclitaxel, and
the neurotoxicity that results appears to be more readily reversible
Vincristine has been effectively combined with prednisone for
remission induction in acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. than is typically observed with paclitaxel.
Docetaxel is a semisynthetic taxane derived from the European
It is also active in various hematologic malignancies such as Hodg- yew tree. Its mechanism of action, metabolism, and elimination
kin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, and multiple myeloma, and are identical to those of paclitaxel. It is approved for use as second-
in several pediatric tumors including rhabdomyosarcoma, neuro- line therapy in advanced breast cancer and NSCLC, and it also
blastoma, Ewing’s sarcoma, and Wilms’ tumor. has major activity in head and neck cancer, small cell lung cancer,
The main dose-limiting toxicity is neurotoxicity, usually
expressed as a peripheral sensory neuropathy, although autonomic gastric cancer, advanced platinum-refractory ovarian cancer, and
bladder cancer. Its major toxicities are listed in Table 54–4.
nervous system dysfunction with orthostatic hypotension, urinary Cabazitaxel is a semisynthetic taxane and its mechanism of
retention, and paralytic ileus or constipation, cranial nerve palsies, action, metabolism, and elimination are identical to those of the
ataxia, seizures, and coma have been observed. While myelosup- other taxanes. However, unlike other taxanes, cabazitaxel is a poor
pression occurs, it is generally milder and much less significant substrate for the multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein efflux pump
than with vinblastine. The other adverse effect that may develop is and may, therefore, be useful for treating multidrug-resistant
the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone tumors. It is approved for use in combination with prednisone in
(SIADH).
the second-line therapy of hormone-refractory metastatic prostate
cancer previously treated with a docetaxel-containing regimen.
Vinorelbine Its major toxicities include myelosuppression, neurotoxicity, and
Vinorelbine is a semisynthetic derivative of vinblastine whose allergic reactions.
mechanism of action is identical to that of vinblastine and vin- Ixabepilone is a semisynthetic epothilone B analog, not
cristine, ie, inhibition of mitosis of cells in the M phase through a taxane, that functions as a microtubule inhibitor and binds
inhibition of tubulin polymerization. This agent has activity in directly to β-tubulin subunits on microtubules, leading to
NSCLC, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer. Myelosuppression inhibition of normal microtubule dynamics. As such, it is active
with neutropenia is the dose-limiting toxicity, but other adverse in the M phase of the cell cycle. This agent is presently approved
effects include nausea and vomiting, transient elevations in liver for metastatic breast cancer in combination with the oral fluoro-
function tests, neurotoxicity, and SIADH. pyrimidine capecitabine or as monotherapy. Of note, this agent
continues to have activity in drug-resistant tumors that overexpress
P-glycoprotein or tubulin mutations. The main adverse effects
TAXANES & OTHER ANTI-MICROTUBULE include myelosuppression, hypersensitivity reactions, and neuro-
DRUGS toxicity in the form of peripheral sensory neuropathy.
Eribulin is a synthetic analog of halichondrin B, and it inhibits
Paclitaxel is an alkaloid ester derived from the Pacific yew (Taxus microtubule function, leading to a block in the G 2 -M phase of the
brevifolia) and the European yew (Taxus baccata). The drug func- cell cycle. This agent appears to be less sensitive to the multidrug
tions as a mitotic spindle poison through high-affinity binding to resistance-mediated P-glycoprotein efflux pump, and one of the