Page 978 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 978
964 SECTION VIII Chemotherapeutic Drugs
advantages of this agent is that it has activity in drug-resistant therapy. The main adverse effects associated with the liposomal
tumors that overexpress P-glycoprotein. It is presently approved formulation are myelosuppression and GI toxicity with diarrhea
for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. and nausea and vomiting. Relatively little is known about the
clinical pharmacology and metabolism of this liposomal formula-
EPIPODOPHYLLOTOXINS tion of irinotecan.
Etoposide is a semisynthetic derivative of podophyllotoxin, which ANTITUMOR ANTIBIOTICS
is extracted from the mayapple root (Podophyllum peltatum). Intra-
venous and oral formulations of etoposide are approved for clini- Screening of microbial products led to the discovery of a number
cal use in the USA. Oral bioavailability is about 50%, requiring of growth-inhibiting compounds that have proved to be clinically
oral dosage to be twice that of intravenous dosage. Up to 30–50% useful in cancer chemotherapy. Many of these antibiotics bind to
of an administered dose of drug is excreted in the urine, and dose DNA through intercalation between specific bases and block the
reduction is required in patients with renal dysfunction. Etoposide synthesis of RNA, DNA, or both; cause DNA strand scission; and
forms a complex with topoisomerase II, the enzyme responsible interfere with cell replication. All of the anti-cancer antibiotics
for cutting and religating double stranded DNA, and DNA, now being used in clinical practice are products of various strains
leading to inhibition of the functional activity of topoisomerase of the soil microbe Streptomyces. These include the anthracyclines,
II with inhibition of DNA synthesis and function. Etoposide has bleomycin, and mitomycin.
clinical activity in germ cell cancer, small cell and NSCLC, Hodg-
kin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, and gastric cancer. Major ANTHRACYCLINES
toxicities are listed in Table 54–4.
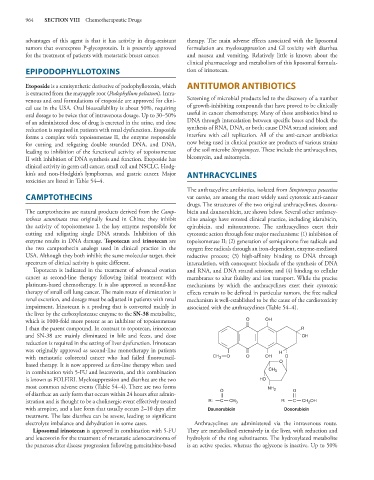
The anthracycline antibiotics, isolated from Streptomyces peucetius
CAMPTOTHECINS var caesius, are among the most widely used cytotoxic anti-cancer
drugs. The structures of the two original anthracyclines, doxoru-
The camptothecins are natural products derived from the Camp- bicin and daunorubicin, are shown below. Several other anthracy-
totheca acuminata tree originally found in China; they inhibit cline analogs have entered clinical practice, including idarubicin,
the activity of topoisomerase I, the key enzyme responsible for epirubicin, and mitoxantrone. The anthracyclines exert their
cutting and religating single DNA strands. Inhibition of this cytotoxic action through four major mechanisms: (1) inhibition of
enzyme results in DNA damage. Topotecan and irinotecan are topoisomerase II; (2) generation of semiquinone free radicals and
the two camptothecin analogs used in clinical practice in the oxygen free radicals through an iron-dependent, enzyme-mediated
USA. Although they both inhibit the same molecular target, their reductive process; (3) high-affinity binding to DNA through
spectrum of clinical activity is quite different. intercalation, with consequent blockade of the synthesis of DNA
Topotecan is indicated in the treatment of advanced ovarian and RNA, and DNA strand scission; and (4) binding to cellular
cancer as second-line therapy following initial treatment with membranes to alter fluidity and ion transport. While the precise
platinum-based chemotherapy. It is also approved as second-line mechanisms by which the anthracyclines exert their cytotoxic
therapy of small cell lung cancer. The main route of elimination is effects remain to be defined in particular tumors, the free radical
renal excretion, and dosage must be adjusted in patients with renal mechanism is well-established to be the cause of the cardiotoxicity
impairment. Irinotecan is a prodrug that is converted mainly in associated with the anthracyclines (Table 54–4).
the liver by the carboxylesterase enzyme to the SN-38 metabolite,
which is 1000-fold more potent as an inhibitor of topoisomerase O OH
I than the parent compound. In contrast to topotecan, irinotecan R
and SN-38 are mainly eliminated in bile and feces, and dose OH
reduction is required in the setting of liver dysfunction. Irinotecan
was originally approved as second-line monotherapy in patients H
with metastatic colorectal cancer who had failed fluorouracil- CH 3 O O OH O
based therapy. It is now approved as first-line therapy when used O
in combination with 5-FU and leucovorin, and this combination CH 3
is known as FOLFIRI. Myelosuppression and diarrhea are the two HO
most common adverse events (Table 54–4). There are two forms NH 2
of diarrhea: an early form that occurs within 24 hours after admin- O O
istration and is thought to be a cholinergic event effectively treated R: C CH 3 R: C CH OH
2
with atropine, and a late form that usually occurs 2–10 days after Daunorubicin Doxorubicin
treatment. The late diarrhea can be severe, leading to significant
electrolyte imbalance and dehydration in some cases. Anthracyclines are administered via the intravenous route.
Liposomal irinotecan is approved in combination with 5-FU They are metabolized extensively in the liver, with reduction and
and leucovorin for the treatment of metastatic adenocarcinoma of hydrolysis of the ring substituents. The hydroxylated metabolite
the pancreas after disease progression following gemcitabine-based is an active species, whereas the aglycone is inactive. Up to 50%