Page 823 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 823
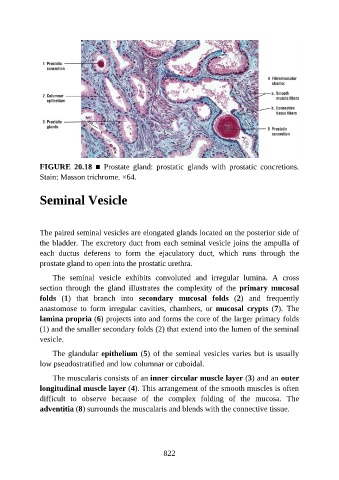
FIGURE 20.18 ■ Prostate gland: prostatic glands with prostatic concretions.
Stain: Masson trichrome. ×64.
Seminal Vesicle
The paired seminal vesicles are elongated glands located on the posterior side of
the bladder. The excretory duct from each seminal vesicle joins the ampulla of
each ductus deferens to form the ejaculatory duct, which runs through the
prostate gland to open into the prostatic urethra.
The seminal vesicle exhibits convoluted and irregular lumina. A cross
section through the gland illustrates the complexity of the primary mucosal
folds (1) that branch into secondary mucosal folds (2) and frequently
anastomose to form irregular cavities, chambers, or mucosal crypts (7). The
lamina propria (6) projects into and forms the core of the larger primary folds
(1) and the smaller secondary folds (2) that extend into the lumen of the seminal
vesicle.
The glandular epithelium (5) of the seminal vesicles varies but is usually
low pseudostratified and low columnar or cuboidal.
The muscularis consists of an inner circular muscle layer (3) and an outer
longitudinal muscle layer (4). This arrangement of the smooth muscles is often
difficult to observe because of the complex folding of the mucosa. The
adventitia (8) surrounds the muscularis and blends with the connective tissue.
822