Page 839 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 839
SECTION 1 Ovary and Uterus: Overview
The human female reproductive system consists of paired internal ovaries,
paired uterine (fallopian) tubes, and a single uterus. Inferior to the uterus and
separated by the cervix is the vagina. Because mammary glands are part of the
female reproductive system, their histologic structure and function are included
in this chapter.
During reproductive life, the human female reproductive organs exhibit
cyclic monthly changes in structure and function that represent the menstrual
cycle. The initial menstrual cycle is called menarche, and when these cycles
eventually cease later in life, this phase represents the menopause.
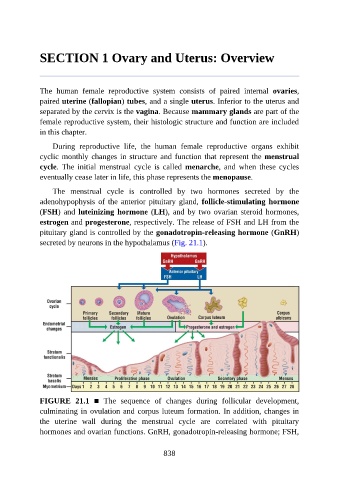
The menstrual cycle is controlled by two hormones secreted by the
adenohypophysis of the anterior pituitary gland, follicle-stimulating hormone
(FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), and by two ovarian steroid hormones,
estrogen and progesterone, respectively. The release of FSH and LH from the
pituitary gland is controlled by the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
secreted by neurons in the hypothalamus (Fig. 21.1).
FIGURE 21.1 ■ The sequence of changes during follicular development,
culminating in ovulation and corpus luteum formation. In addition, changes in
the uterine wall during the menstrual cycle are correlated with pituitary
hormones and ovarian functions. GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; FSH,
838