Page 841 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 841
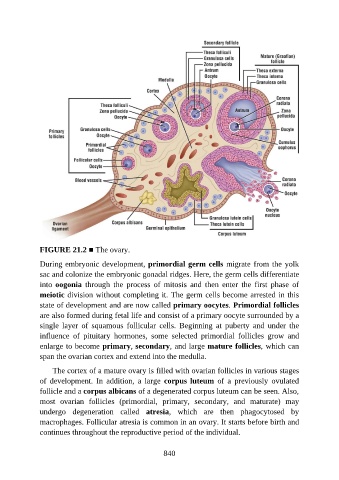
FIGURE 21.2 ■ The ovary.
During embryonic development, primordial germ cells migrate from the yolk
sac and colonize the embryonic gonadal ridges. Here, the germ cells differentiate
into oogonia through the process of mitosis and then enter the first phase of
meiotic division without completing it. The germ cells become arrested in this
state of development and are now called primary oocytes. Primordial follicles
are also formed during fetal life and consist of a primary oocyte surrounded by a
single layer of squamous follicular cells. Beginning at puberty and under the
influence of pituitary hormones, some selected primordial follicles grow and
enlarge to become primary, secondary, and large mature follicles, which can
span the ovarian cortex and extend into the medulla.
The cortex of a mature ovary is filled with ovarian follicles in various stages
of development. In addition, a large corpus luteum of a previously ovulated
follicle and a corpus albicans of a degenerated corpus luteum can be seen. Also,
most ovarian follicles (primordial, primary, secondary, and maturate) may
undergo degeneration called atresia, which are then phagocytosed by
macrophages. Follicular atresia is common in an ovary. It starts before birth and
continues throughout the reproductive period of the individual.
840