Page 913 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 913
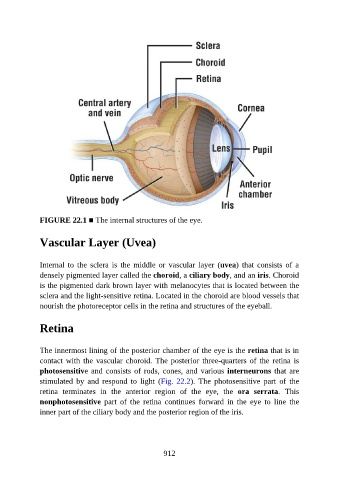
FIGURE 22.1 ■ The internal structures of the eye.
Vascular Layer (Uvea)
Internal to the sclera is the middle or vascular layer (uvea) that consists of a
densely pigmented layer called the choroid, a ciliary body, and an iris. Choroid
is the pigmented dark brown layer with melanocytes that is located between the
sclera and the light-sensitive retina. Located in the choroid are blood vessels that
nourish the photoreceptor cells in the retina and structures of the eyeball.
Retina
The innermost lining of the posterior chamber of the eye is the retina that is in
contact with the vascular choroid. The posterior three-quarters of the retina is
photosensitive and consists of rods, cones, and various interneurons that are
stimulated by and respond to light (Fig. 22.2). The photosensitive part of the
retina terminates in the anterior region of the eye, the ora serrata. This
nonphotosensitive part of the retina continues forward in the eye to line the
inner part of the ciliary body and the posterior region of the iris.
912