Page 177 - Maxwell House
P. 177
POYNTING's THEOREM 157
∫ ∘ = ∬ 1 (∫ ) = ( ) ( )
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
� (3.106)
1
∫ ∘ = ∬ (∫ ) = ( ) ( )
2
1
2
1
1
2
2
2
2
Therefore,
⁄
( ) ( ) = ( ) ( )⁄⁄ 1 1 2 1 2 2 [V = Ω] (3.107)
1
2
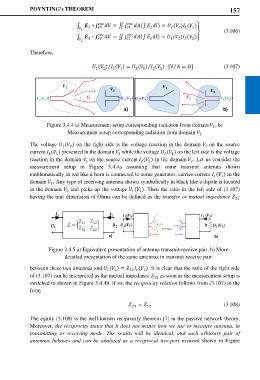
a) b)
Figure 3.4.4 a) Measurement setup corresponding radiation from domain , b)
1
Measurement setup corresponding radiation from domain
2
The voltage ( ) on the right side is the voltage reaction in the domain on the source
2
1
2
current ( ) presented in the domain while the voltage ( ) on the left side is the voltage
1 1 1 2 1
reaction in the domain on the source current ( ) in the domain . Let us consider the
1
2
2
2
measurement setup in Figure 3.4.4a assuming that some transmit antenna shown
emblematically in red like a horn is connected to some generator, carries current ( ) in the
1
1
domain . Any type of receiving antenna shown symbolically in black like a dipole is located
1
in the domain and picks up the voltage ( ). Then the ratio in the left side of (3.107)
2
1
2
having the unit dimension of Ohms can be defined as the transfer or mutual impedance
21
Figure 3.4.5 a) Equivalent presentation of antenna transmit-receive pair, b) More
detailed presentation of the same antennas in transmit-receive pair
between these two antennas and ( ) = ( ). It is clear that the ratio of the right side
21 1
1
1
2
of (3.107) can be interpreted as the mutual impedance as soon as the measurement setup is
12
switched to shown in Figure 3.4.4b. If so, the reciprocity relation follows from (3.107) in the
form
21 = (3.108)
12
The equity (3.108) is the well-known reciprocity theorem [7] in the passive network theory.
Moreover, the reciprocity states that it does not matter how we use or measure antenna, in
transmitting or receiving mode. The results will be identical, and such arbitrary pair of
antennas behaves and can be analyzed as a reciprocal two-port network shown in Figure