Page 218 - Maxwell House
P. 218
198 ANTENNA BASICS
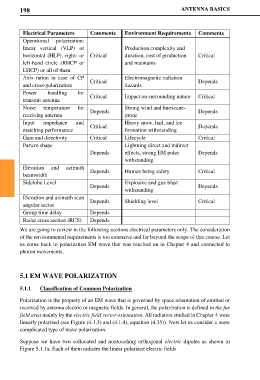
Electrical Parameters Comments Environment Requirements Comments
Operational polarization:
linear vertical (VLP) or Production complexity and
horizontal (HLP), right- or Critical duration, cost of production Critical
left-hand circle (RHCP or and maintains
LHCP) or all of them
Axis ration in case of CP Critical Electromagnetic radiation Depends
and cross-polarization hazards
Power handling for
transmit antenna Critical Impact on surrounding nature Critical
Noise temperature for Strong wind and hurricane-
receiving antenna Depends prone Depends
Input impedance and Heavy snow, hail, and ice
matching performance Critical formation withstanding Depends
Gain and directivity Critical Lifecycle Critical
Pattern shape Lightning direct and indirect
Depends effects, strong EM pulse Depends
withstanding
Elevation and azimuth
beamwidth Depends Human being safety Critical
Sidelobe Level Explosive and gun blast
Depends Depends
withstanding
Elevation and azimuth scan Depends Shielding level Critical
angular sector
Group time delay Depends
Radar cross section (RCS) Depends
We are going to review in the following sections electrical parameters only. The consideration
of the environmental requirements is too extensive and far beyond the scope of this course. Let
us come back to polarization EM wave that was touched on in Chapter 4 and connected to
photon movements.
5.1 EM WAVE POLARIZATION
5.1.1 Classification of Common Polarization
Polarization is the property of an EM wave that is governed by space orientation of emitted or
received by antenna electric or magnetic fields. In general, the polarization is defined in the far
field area mainly by the electric field vector orientation. All radiators studied in Chapter 4 were
linearly polarized (see Figure (4.1.3) and (4.1.4), equation (4.35)). Now let us consider a more
complicated type of wave polarization.
Suppose we have two collocated and nontouching orthogonal electric dipoles as shown in
Figure 5.1.1a. Each of them radiates the linear polarized electric fields