Page 55 - March 2020 - WT Site
P. 55
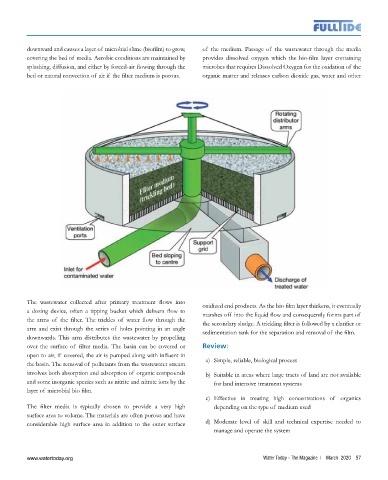
downward and causes a layer of microbial slime (biofilm) to grow, of the medium. Passage of the wastewater through the media
covering the bed of media. Aerobic conditions are maintained by provides dissolved oxygen which the bio-film layer containing
splashing, diffusion, and either by forced-air flowing through the microbes that requires Dissolved Oxygen for the oxidation of the
bed or natural convection of air if the filter medium is porous. organic matter and releases carbon dioxide gas, water and other
The wastewater collected after primary treatment flows into oxidized end products. As the bio film layer thickens, it eventually
a dosing device, often a tipping bucket which delivers flow to marshes off into the liquid flow and consequently forms part of
the arms of the filter. The trickles of water flow through the the secondary sludge. A trickling filter is followed by a clarifier or
arm and exist through the series of holes pointing in an angle sedimentation tank for the separation and removal of the film.
downwards. This arm distributes the wastewater by propelling
over the surface of filter media. The basin can be covered or Review:
open to air, if covered, the air is pumped along with influent in
the basin. The removal of pollutants from the wastewater stream a) Simple, reliable, biological process
involves both absorption and adsorption of organic compounds b) Suitable in areas where large tracts of land are not available
and some inorganic species such as nitrite and nitrate ions by the for land intensive treatment systems
layer of microbial bio film.
c) Effective in treating high concentrations of organics
The filter media is typically chosen to provide a very high depending on the type of medium used
surface area to volume. The materials are often porous and have
considerable high surface area in addition to the outer surface d) Moderate level of skill and technical expertise needed to
manage and operate the system
Water Today - The Magazine l March 2020 57